Health Conditions You Should Know About
When it comes to health, knowing the facts about common conditions can make a huge difference. Whether you're curious about growths like lesions and tumors or looking into treatment options for erectile dysfunction, having clear, straightforward info helps you stay ahead and make smart decisions.
Lesions vs. Tumors: What's the Difference?
You've probably heard the terms lesion and tumor, but what's the real deal between them? Lesions are usually harmless and can pop up because of infections, injuries, or other triggers. Tumors, on the other hand, are a bit trickier—they can be harmless or cancerous. Unlike lesions, tumors might spread if not treated. This means that while lesions often need simple medication like antibiotics, tumors might require stronger treatments such as surgery or chemotherapy.
Feeling a lump or noticing unusual growth? Don’t ignore it. Early check-ups can help catch things before they get serious.
Understanding Uterine Cancer Spread
Uterine cancer starts in the lining of the uterus and can spread if left unchecked. It often travels through the lymph nodes and bloodstream to places like the lungs. Some factors like age, weight, and hormone use can raise your risk. Treatments include surgery, radiation, and chemo, depending on how far it has spread.
Knowing your risk helps you catch warning signs early. Talk to a doctor if symptoms or concerns pop up.
From sexual health issues like erectile dysfunction—where options like Vardenafil and Tadalafil come into play—to understanding cancers and growths, getting the facts matters. Choosing the right meds or treatments depends on clear info and your lifestyle needs. At TL-Pharmacy, we're here to give you straight answers without the jargon, so you can feel confident about your health decisions.
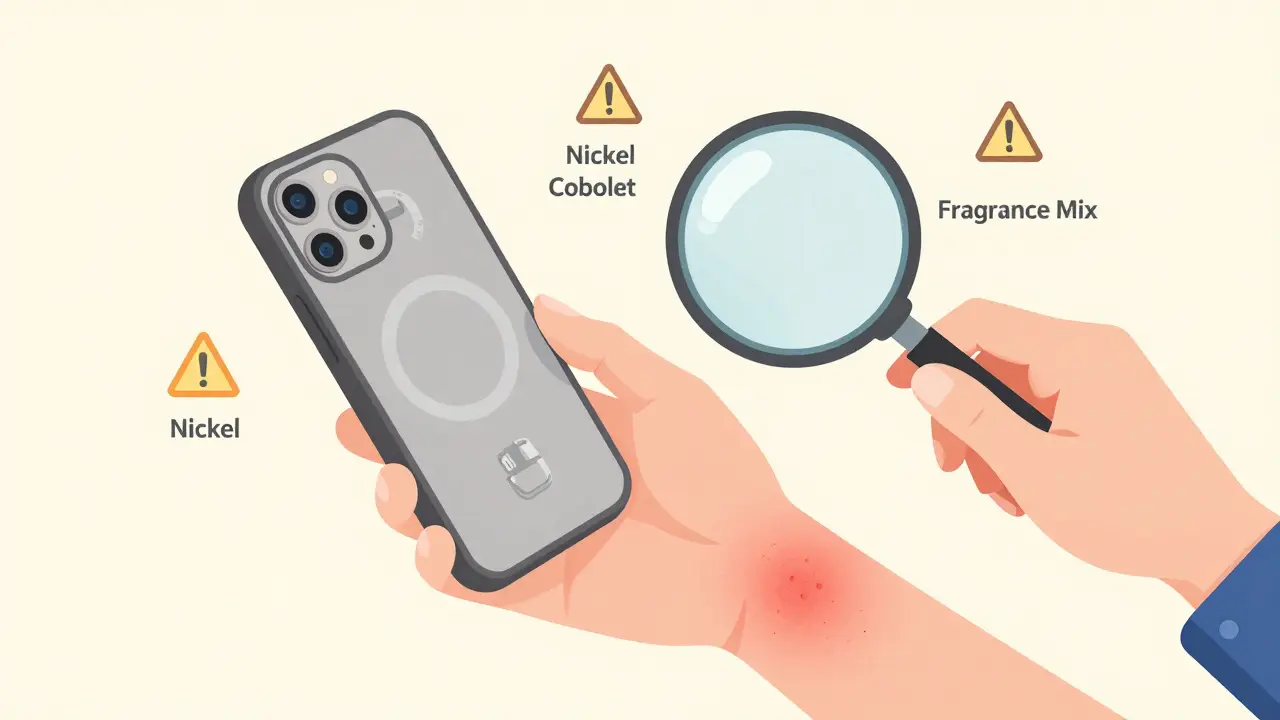
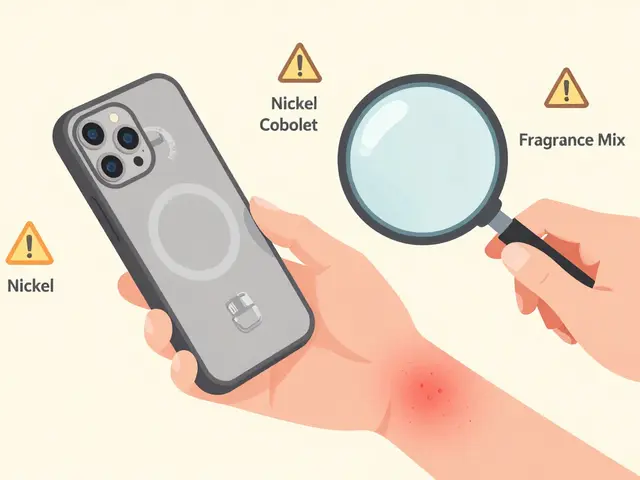
Contact Dermatitis: How to Identify and Avoid Allergens That Trigger Skin Reactions
Learn how to identify and avoid the allergens causing your skin rash. Patch testing is the key to finding hidden triggers like nickel, fragrance, and cobalt-and avoiding them can clear your skin for good.
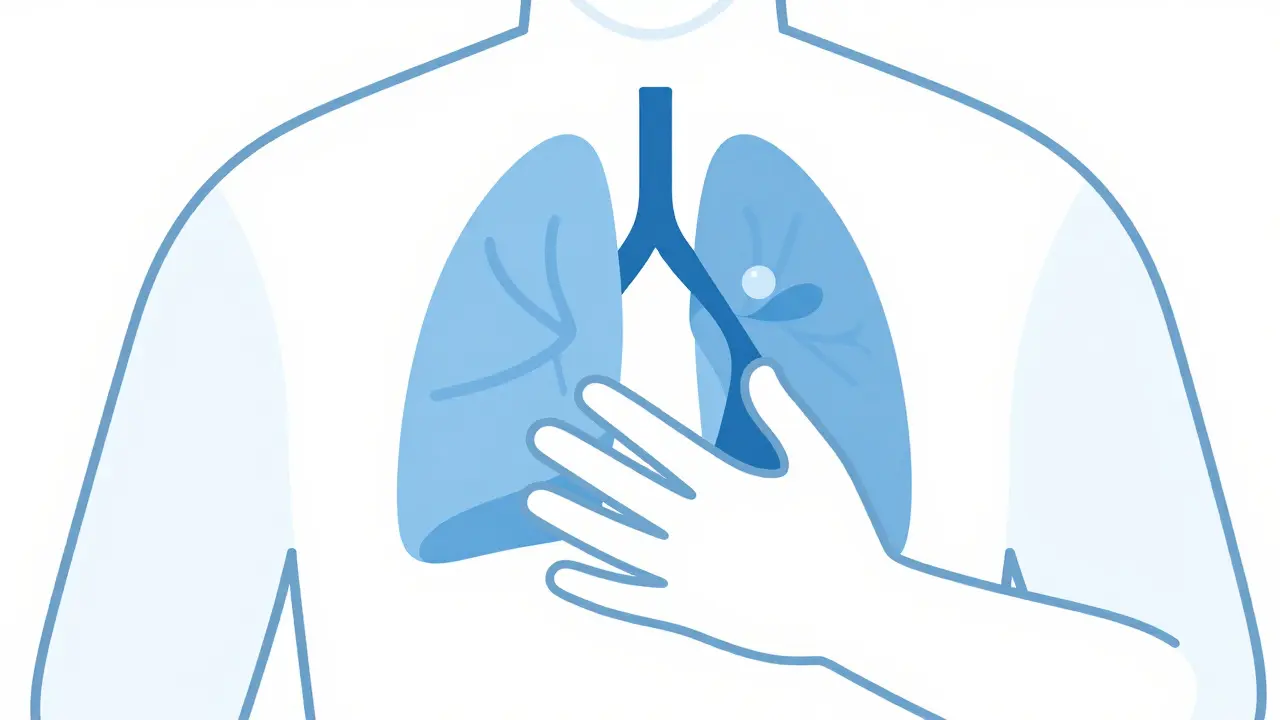
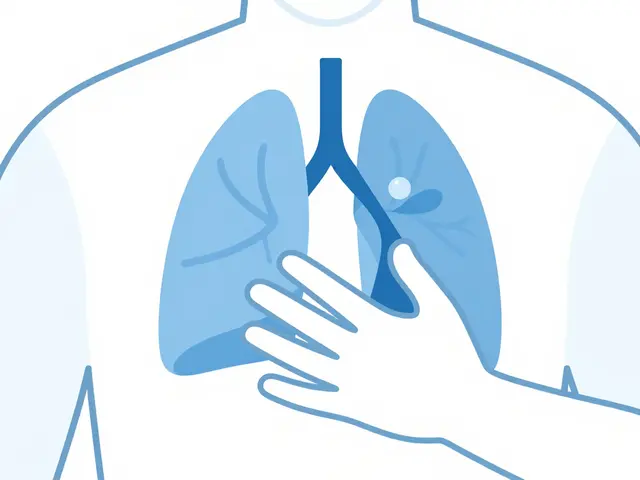
Pneumothorax: Recognizing Symptoms and Getting Emergency Care Fast
Pneumothorax, or collapsed lung, is a medical emergency. Learn key symptoms like sharp chest pain and shortness of breath, why immediate care is critical, and what to expect during treatment.
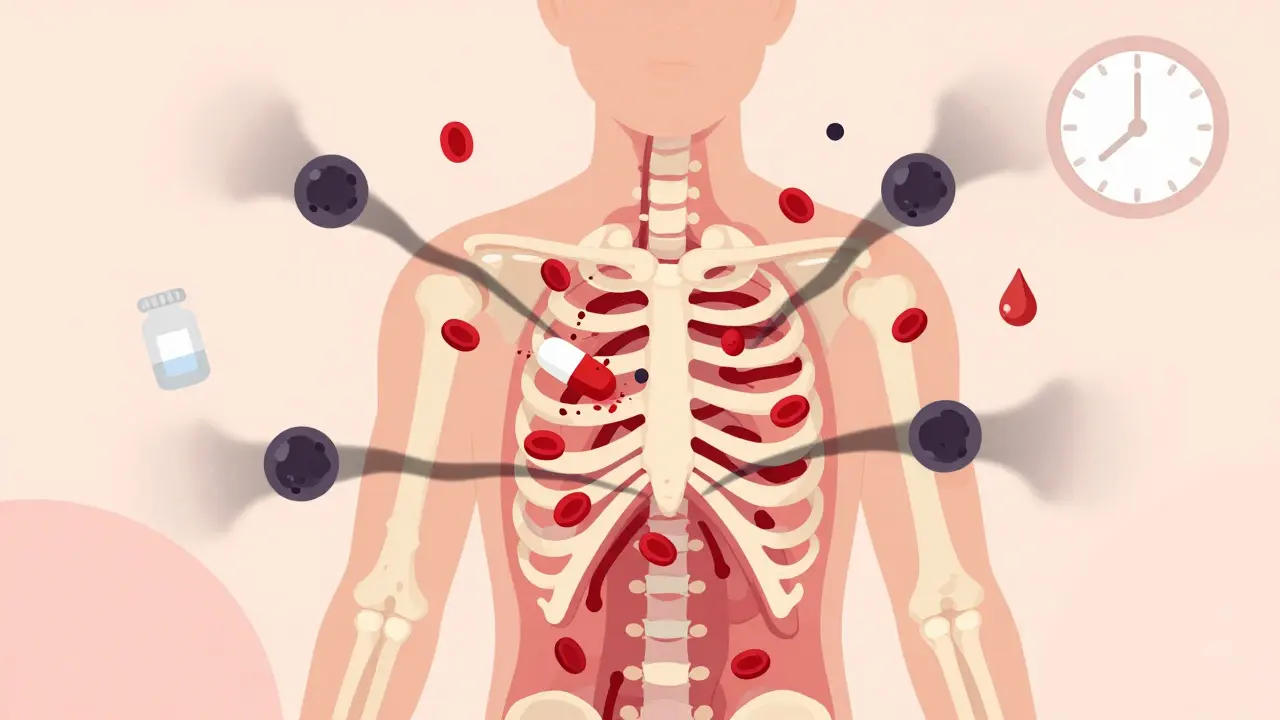
Aplastic Anemia from Medications: Early Signs and Urgent Actions
Medication-induced aplastic anemia is rare but deadly if missed. Learn the early warning signs - fatigue, bruising, fevers - and the urgent steps to take if you're on high-risk drugs like carbamazepine or chloramphenicol.
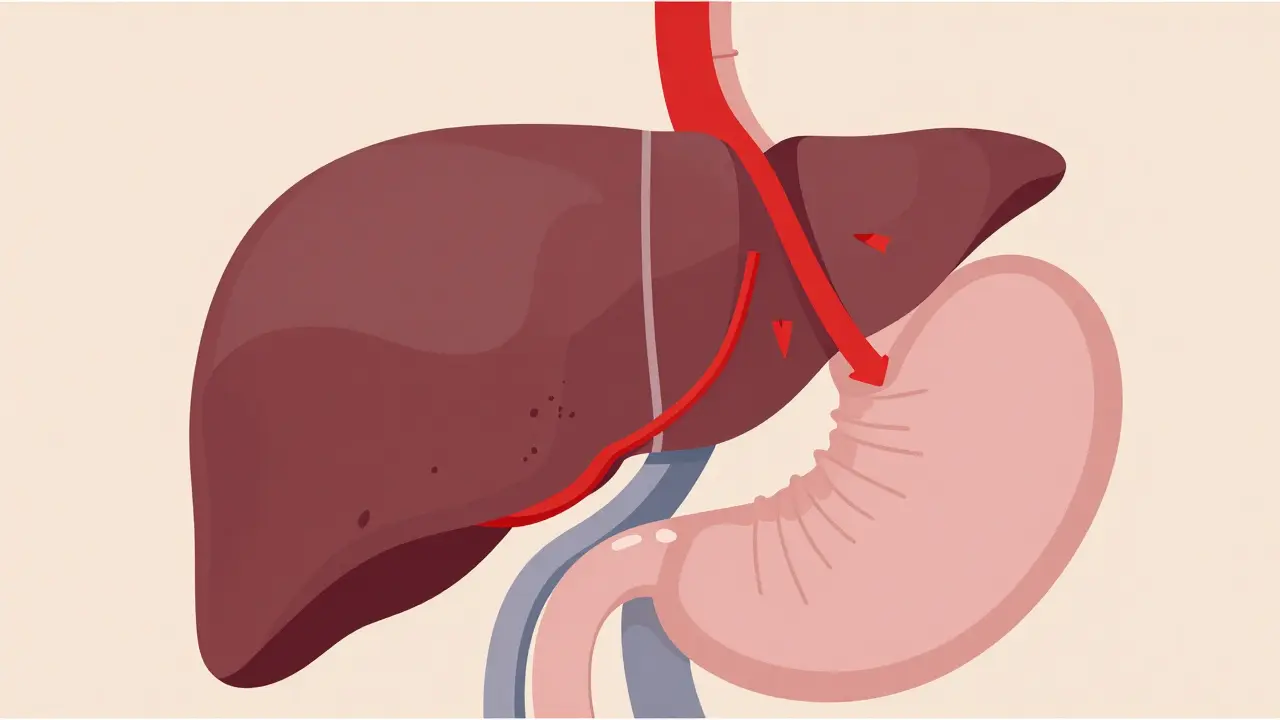
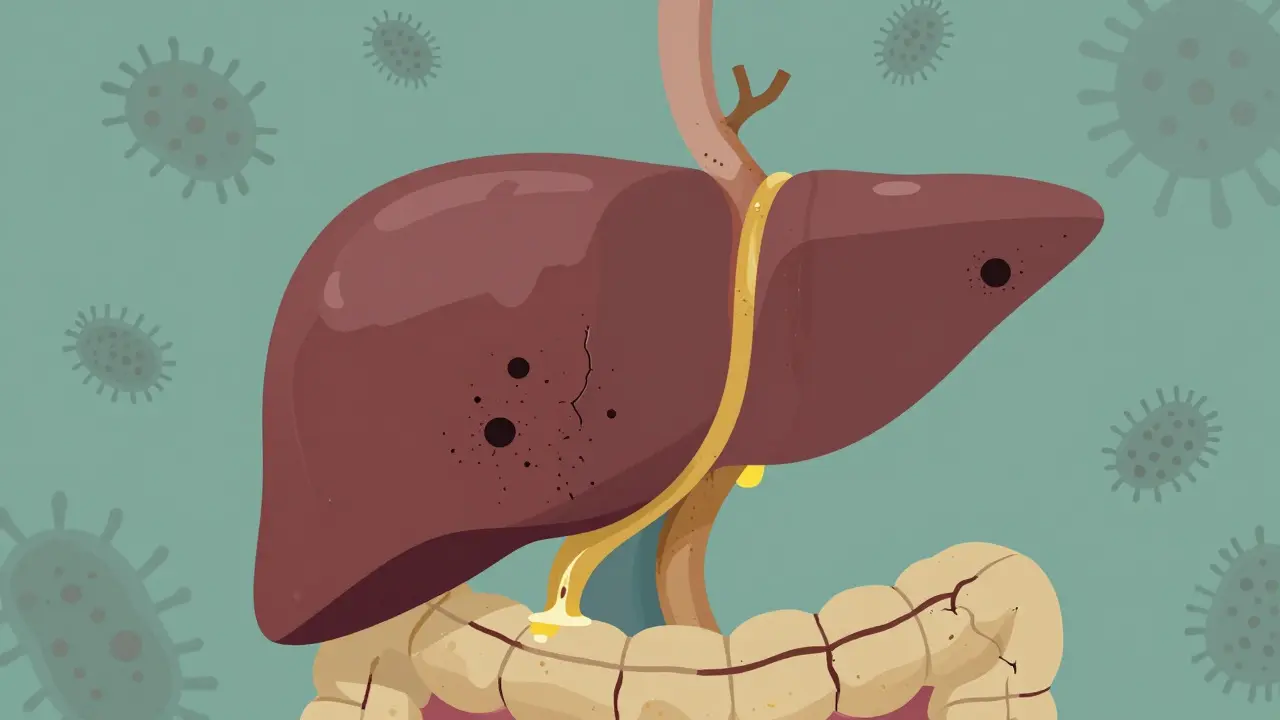
Portal Hypertension: Managing Varices, Ascites, and Life-Threatening Complications
Portal hypertension is a dangerous rise in liver blood pressure that causes varices, ascites, and life-threatening complications. Learn how to manage bleeding risks, fluid buildup, and emerging treatments in 2026.
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: Understanding the Progressive Bile Duct Disease
Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a rare, progressive liver disease that damages bile ducts, leading to scarring and liver failure. No cure exists, but early diagnosis and specialized care can manage symptoms and delay complications.
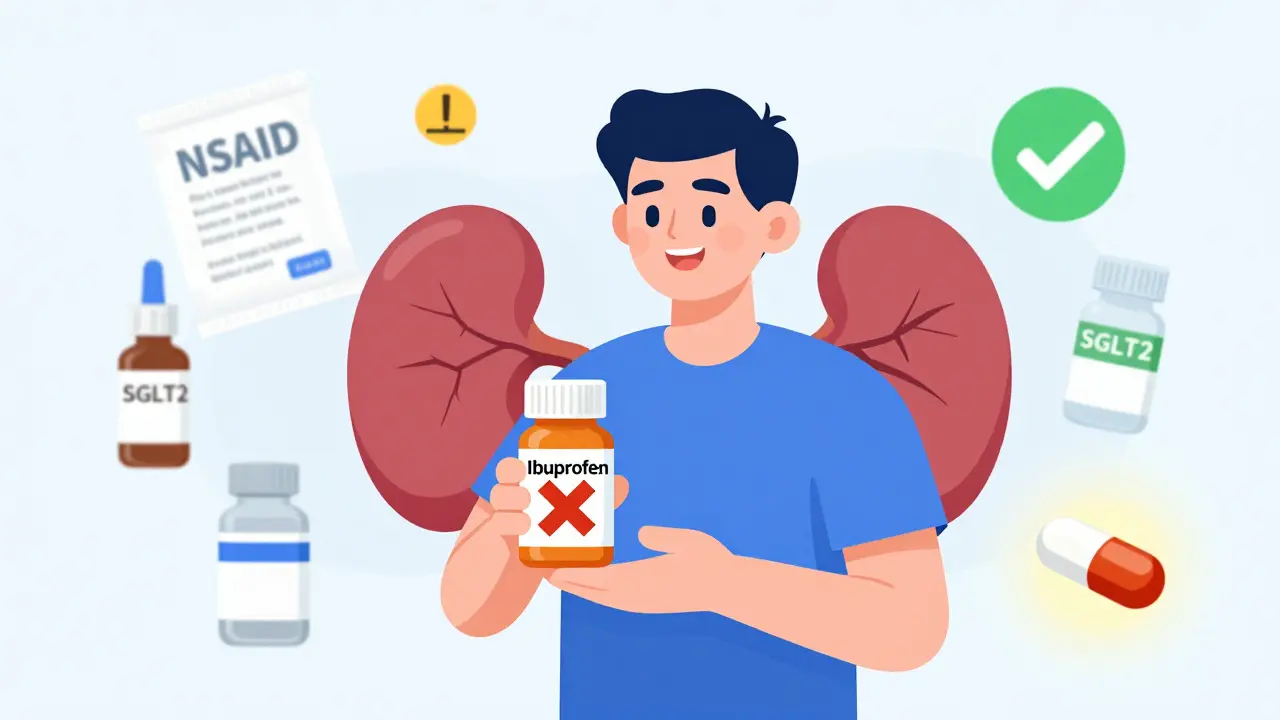
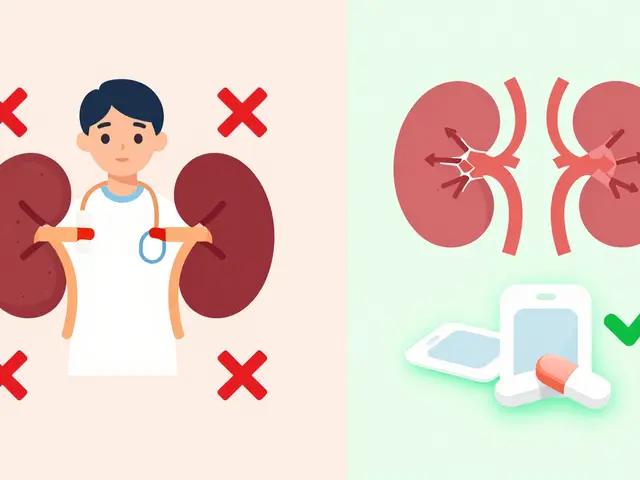
Medication Safety in Kidney Disease: How to Avoid Nephrotoxins and Get the Right Dose
Learn how to safely take medications with kidney disease-avoid nephrotoxins, adjust doses based on eGFR, and use the latest guidelines to protect your kidneys from drug-related harm.
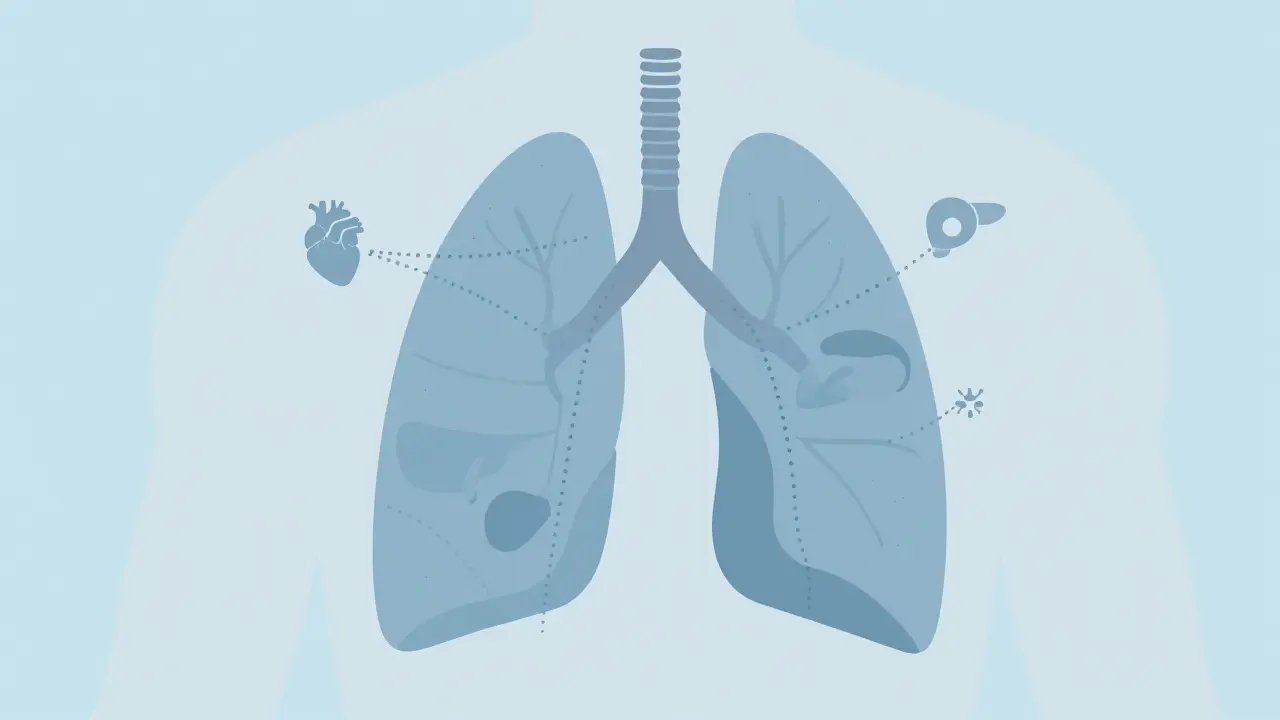
Pleural Effusion: Causes, Thoracentesis, and How to Prevent Recurrence
Pleural effusion causes breathing trouble and can signal heart failure, pneumonia, or cancer. Learn how thoracentesis works, what fluid tests reveal, and how to prevent recurrence with modern treatments like indwelling catheters.
Multiple Sclerosis: Understanding Neurological Deterioration and How Disease-Modifying Therapies Work
Multiple sclerosis involves more than relapses - it's a slow neurological decline caused by irreversible axon damage. Learn how current treatments help, why they fall short in progressive MS, and what new therapies are emerging to protect the brain.
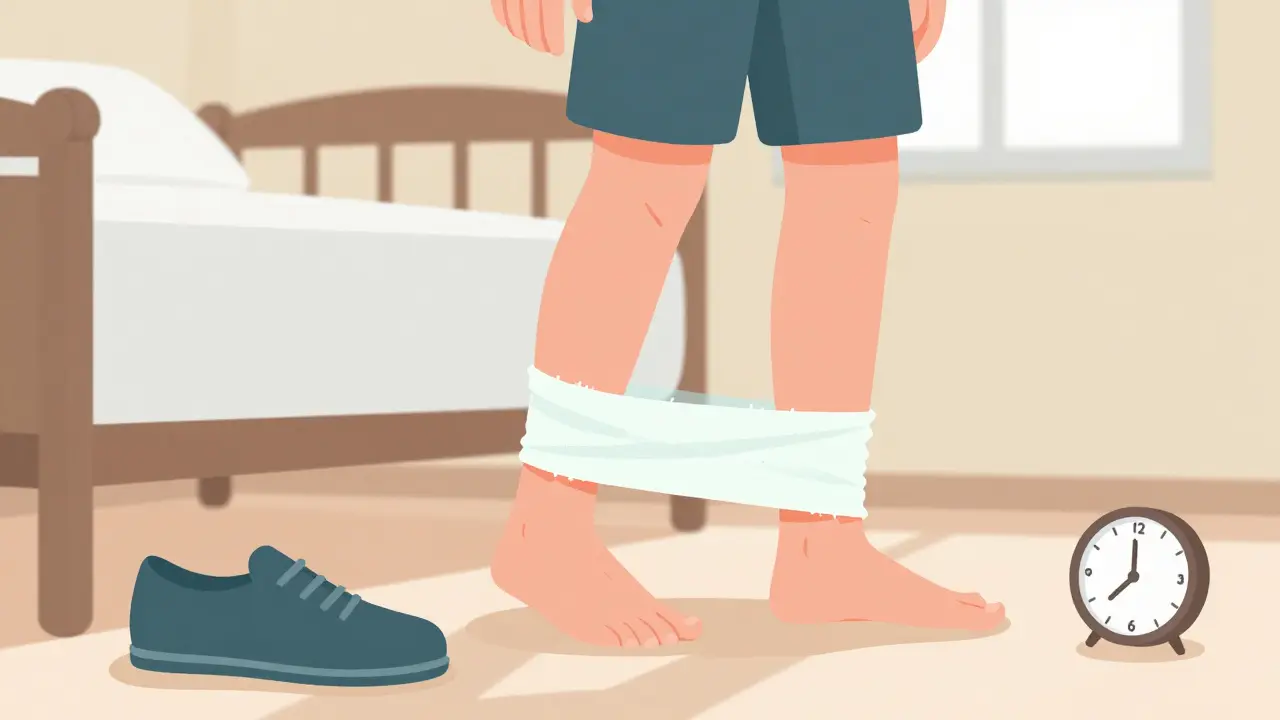
Plantar Fasciitis: Understanding Heel Pain Causes and Effective Treatment Options
Plantar fasciitis, now called plantar fasciopathy, is a common cause of heel pain caused by tissue degeneration, not inflammation. Learn the real causes, what treatments actually work, and how to avoid common mistakes that delay recovery.
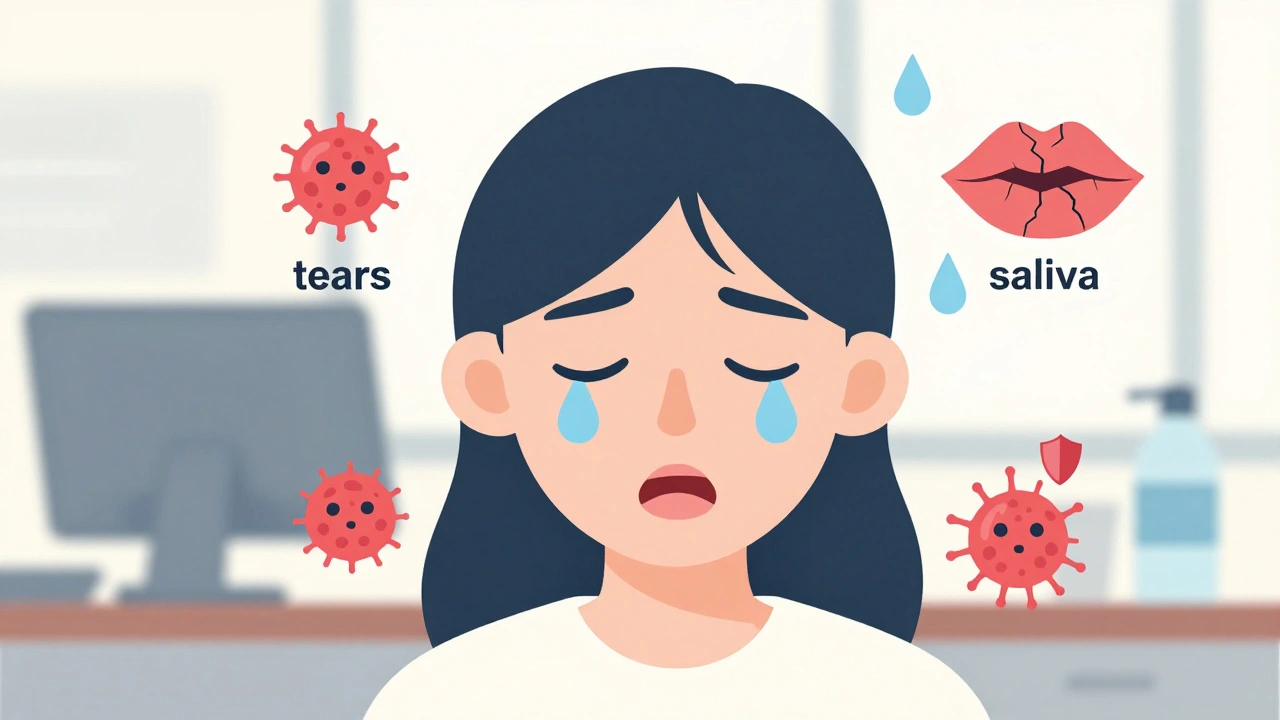
Sjögren’s Syndrome: What It Is, How It Affects Your Body, and What You Can Do
Sjögren’s Syndrome is an autoimmune disease that attacks moisture-producing glands, causing chronic dry eyes, dry mouth, fatigue, and joint pain. Learn how it's diagnosed, managed, and why early detection matters.
- 1
- 2