Blood Pressure Medications: Types, Options, and What Works Best
When your blood pressure stays too high, it puts extra strain on your heart, arteries, and organs. That’s where blood pressure medications, drugs designed to lower and control elevated blood pressure. Also known as antihypertensive drugs, they help reduce the risk of stroke, heart attack, and kidney damage. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution—what works for one person might not work for another. Doctors pick these meds based on your age, other health issues, side effects, and how your body responds.
Common types include ACE inhibitors, medications that relax blood vessels by blocking a hormone that narrows them, like lisinopril and enalapril. Then there are beta blockers, drugs that slow your heart rate and reduce the force of your heartbeat, such as metoprolol and atenolol. Diuretics, calcium channel blockers, and ARBs are also widely used. Each group works differently, and sometimes doctors combine them for better control. Side effects can range from dizziness and dry cough to fatigue or swelling—but not everyone gets them, and many improve over time.
What you won’t find in most guides is how real people navigate these choices. Some switch meds because of cost. Others stop because of side effects they didn’t know were normal. A few find one drug that just clicks—no headaches, no dizziness, steady numbers. The posts below cover exactly that: real comparisons between common drugs, what to watch for, how to talk to your doctor, and what alternatives exist when the first option doesn’t fit. Whether you’re new to treatment or switching meds after years, you’ll find practical, no-fluff advice here.
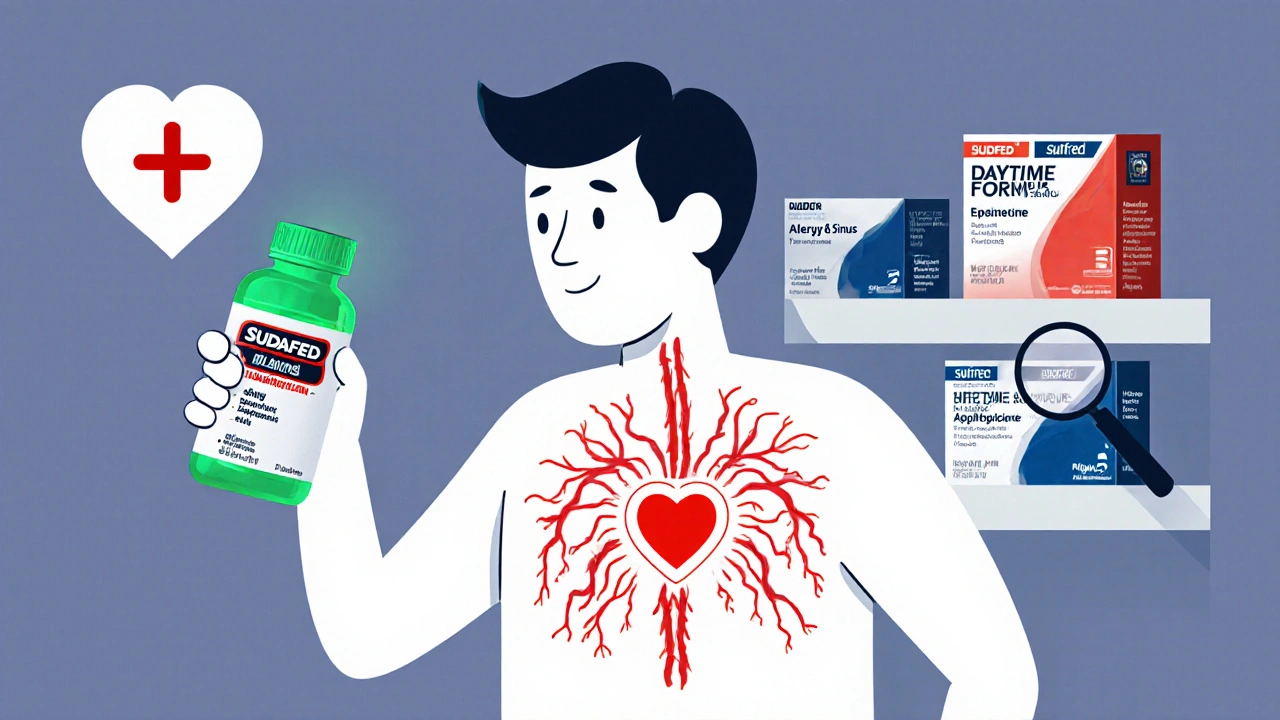
Nasal Decongestants and Blood Pressure Medications: What You Need to Know for Safe Use
Nasal decongestants can dangerously raise blood pressure and interfere with hypertension meds. Learn which ingredients to avoid, safer alternatives, and how to use cold medicine safely if you have high blood pressure.