Sneezing & Smell Loss Symptom Checker
Assess Your Symptoms
Answer these questions to identify potential causes of your sneezing and smell loss.
Frequency of sneezing
Duration of symptoms
Smell loss severity
Additional symptoms
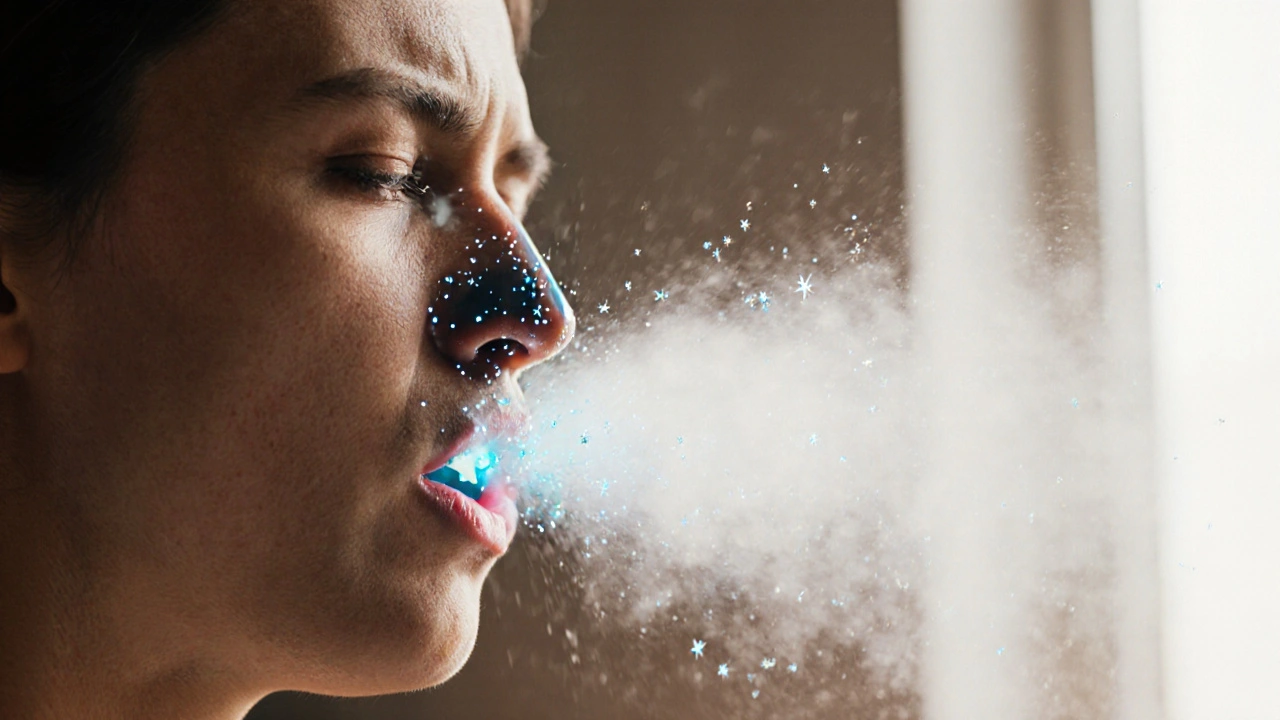
Ever notice that after a big sneeze your world seems a little quieter? That’s not just imagination-sneezing can actually interfere with how well you smell. Below we’ll break down what’s happening inside your nose, why certain illnesses make the connection stronger, and what you can do to keep your sense of smell sharp.
What the Olfactory System Does
Olfactory system is a network of receptors, nerves, and brain regions that detects airborne chemicals and translates them into the perception of smell. It starts with tiny olfactory receptor neurons lining the upper part of the nasal cavity. When odor molecules bind to these receptors, signals travel along the olfactory nerve to the olfactory bulb, then on to the brain’s limbic system where memory and emotion meet.
Because the olfactory epithelium sits just behind the front of the nasal passages, any change in airflow or mucus can quickly affect how many odor molecules actually reach the receptors.
Why a Sneeze Can Blank Out Your Nose
Sneezing is the body’s rapid, forceful expulsion of air meant to clear irritants from the nasal lining. While it’s a useful defense, the sneeze does three things that can temporarily dampen smell:
- Airflow disruption: A sneeze can flush the nasal passage, pushing mucus and odor‑binding particles out before they have a chance to bind to receptors.
- Transient swelling: The sudden burst of pressure triggers a brief inflammatory response, swelling the lining of the nasal cavity and narrowing the pathway for odor molecules.
- Receptor reset: Intense airflow can temporarily desensitize olfactory receptor neurons, similar to how a loud noise can dull hearing for a moment.
These effects usually last only seconds to a few minutes, but if sneezing is frequent, the cumulative impact can feel more noticeable.
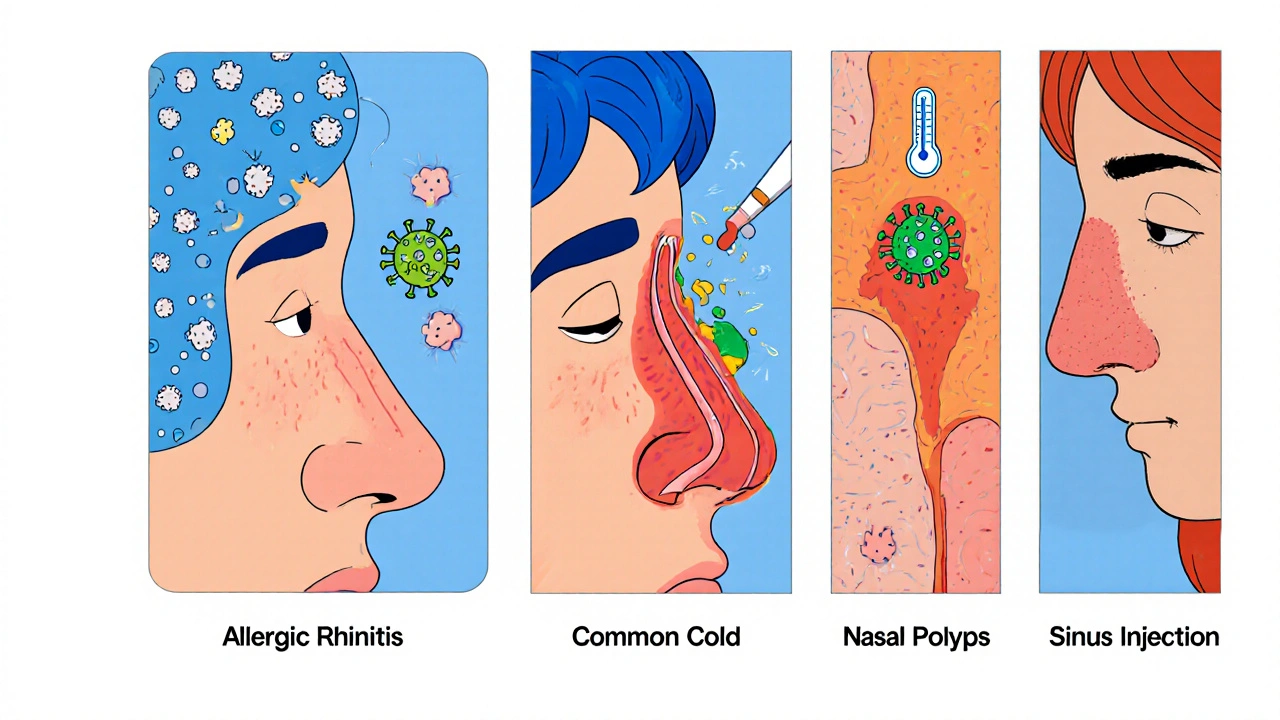
Health Conditions That Pair Sneezing with Smell Loss
When sneezing becomes chronic, it often signals an underlying condition that also messes with your sense of smell. Here are the most common culprits:
| Condition | Typical Sneezing Frequency | Effect on Smell | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allergic rhinitis | Multiple bouts daily | Temporary reduction, may become chronic anosmia | Seasonal or year‑round |
| Common cold | Intermittent, 2‑5 per day | Congestion‑related smell loss, usually resolves | 7‑10 days |
| COVID‑19 | Often minimal, but can include sudden sneezing | Sudden, sometimes long‑lasting loss (anosmia) | Weeks to months |
| Nasal polyps | Occasional | Persistent reduced smell due to blockage | Chronic |
| Sinus infection | Variable, often triggered by irritation | Significant loss during inflammation | 2‑4 weeks |
Notice how each condition pairs a sneezing pattern with a specific type of smell disruption. Understanding this link helps you decide whether a simple home remedy will do, or if a doctor’s visit is needed.
Red Flags: When a Sneeze Isn’t Just a Sneeze
Most occasional sneezes are harmless, but keep an eye out for these warning signs:
- Loss of smell lasting more than two weeks without improvement.
- Frequent sneezing (more than 5‑6 times a day) accompanied by thick, discolored mucus.
- Facial pain, fever, or swelling around the eyes-possible sinus infection.
- Recent COVID‑19 exposure and sudden anosmia.
- Persistent nasal blockage despite using over‑the‑counter decongestants.
If any of these appear, it’s time to see a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis can prevent permanent damage to the olfactory nerves.

Practical Steps to Keep Your Smell Sharp
Below are actionable tips you can start using today. They target the three mechanisms we discussed-airflow, swelling, and receptor reset.
- Stay hydrated: Thin mucus, making it easier for odor molecules to reach receptors.
- Use saline nasal irrigation: A gentle rinse clears out irritants and reduces swelling without medication.
- Consider antihistamines: For allergic rhinitis, non‑sedating antihistamines cut the histamine‑driven sneezing burst.
- Limit irritants: Smoke, strong perfumes, and dust trigger sneezing and can inflame the olfactory epithelium.
- Practice good hand hygiene: Reducing viral infections (like the common cold or COVID‑19) protects both your nose and your sense of smell.
- Check for nasal polyps: If you notice chronic blockage, an ENT specialist can assess and treat polyps, often restoring smell.
Remember, these measures work best when combined-hydration + nasal rinse + avoiding triggers can dramatically cut down the sneezing‑smell cycle.
FAQs About Sneezing and Smell
Can a single sneeze permanently damage my sense of smell?
Can a single sneeze permanently damage my sense of smell?
No. An isolated sneeze might momentarily dampen smell, but permanent loss (anosmia) usually stems from prolonged inflammation, infection, or structural issues like polyps.
Why do I still smell less even after my sneezing stops?
Why do I still smell less even after my sneezing stops?
Residual swelling or mucus can keep the olfactory epithelium blocked. In conditions like allergic rhinitis, the inflammation may linger after sneezing subsides, requiring treatment to clear the blockage.
Is loss of smell a common symptom of COVID‑19?
Is loss of smell a common symptom of COVID‑19?
Yes. Sudden anosmia, often without nasal congestion, became one of the hallmark signs of COVID‑19. Recovery varies; some regain smell within weeks, others take months.
Can nasal sprays help protect my sense of smell?
Can nasal sprays help protect my sense of smell?
Steroid nasal sprays reduce inflammation in chronic allergic rhinitis or sinusitis, improving airflow and often restoring smell when used under a doctor’s guidance.
When should I see an ENT specialist?
When should I see an ENT specialist?
If you experience persistent loss of smell for more than two weeks, chronic nasal blockage, recurring sinus infections, or suspect nasal polyps, schedule an appointment with an ENT doctor for imaging and possible endoscopic evaluation.




Jo D October 12, 2025
Oh great, another piece tellin us that a sneeze can mess with your olfactory receptors – like we needed a PhD in nasal physics to figure that out. The whole airflow‑disruption theory is basically just a fancy way of saying “you blew your nose, uh‑uh”. And don’t get me started on the “receptor reset” jargon, sounds like a sci‑fi reboot for your nose. Anyway, stay hydrated, use a saline rinse, and maybe stop sniffin’ all that pepper if you wanna avoid the sneeze‑smell cycle.
Sinead McArdle October 21, 2025
I appreciate the thorough breakdown of the mechanisms involved.
Katherine Krucker Merkle October 29, 2025
Totally get where you’re coming from – it’s fascinating how a simple sneeze can temporarily tweak the olfactory pathway. I’ve noticed my own sense of smell dip right after a big sneeze, especially when I’m fighting allergies. Keeping the nasal passages clear with a saline spray really seems to help. Also, staying well‑hydrated makes the mucus less viscous, so odor molecules can reach the receptors better. Cheers for the practical tips!
Mark Quintana November 5, 2025
i read the article and it kinda makes sense, but the whole "receptor reset" thing sounded a bit off to me. I mean, sneezin’ does cause a pressure change, but i guess it could just be the swelling that blocks stuff. Also, i’ve been using a neti pot and it does help a lot. maybe try an antihistamine if allergies are the cause. stay safe!
Brandon Cassidy November 11, 2025
When we contemplate the sneeze as a physiological event, we must first acknowledge its role as a protective reflex, a sudden expulsion of air designed to clear the nasal mucosa of irritants. Yet this very act, in its urgency, creates a transient turbulence that can displace odor‑laden particles before they have the opportunity to bind to olfactory receptor neurons. The ensuing brief inflammation induces swelling of the nasal epithelium, narrowing the conduit through which scent molecules travel. Simultaneously, the mechanical stress may induce a temporary desensitization of the receptor cells, akin to auditory fatigue after a loud noise. This triad of airflow disruption, mucosal edema, and neuronal reset explains the fleeting anosmia witnessed after a robust sneeze. Moreover, when the sneezing is chronic, as seen in allergic rhinitis or sinusitis, the cumulative effect can lead to a more persistent reduction in olfactory acuity. Chronic inflammation can remodel the olfactory epithelium, diminishing the density of functional receptors. The presence of nasal polyps further obstructs the passage, creating a physical barrier that hinders odorant diffusion. In the case of viral infections such as COVID‑19, the virus may directly damage the olfactory neuroepithelium, compounding the mechanical effects of sneezing. Therapeutically, interventions that address each mechanism prove most effective: saline irrigation clears mucus, corticosteroid sprays reduce inflammation, and antihistamines mitigate allergic triggers. Hydration remains a foundational measure, ensuring mucus remains thin enough for odorants to permeate. Lastly, regular monitoring of olfactory function can alert clinicians to early signs of chronic impairment, prompting timely referral to an otolaryngologist. In sum, the sneeze, while a simple reflex, orchestrates a complex interplay of physical and biochemical events that can temporarily mute our sense of smell, and under persistent conditions, may herald deeper pathology.
Michelle Guatato November 15, 2025
They don’t want you to know that the sneeze‑smell link is a cover‑up for the government’s secret nasal monitoring program. Every time you sneeze, tiny sensors in the airways could be picking up on chemical signatures that they feed into the Big Data brain. Don’t be fooled by the “stay hydrated” advice – it’s just a distraction while they harvest your biometric data. Keep your windows shut, use a HEPA filter, and consider a DIY copper mask if you value your freedom.
Gabrielle Vézina November 19, 2025
Oh, the drama of a sneeze stealing your scents – truly a tragedy of epic proportions.
carl wadsworth November 22, 2025
Let’s keep this civil: nasal hygiene is essential, folks. A saline rinse can clear out the debris that fuels both sneezing and olfactory loss. If you’re dealing with chronic issues, see an ENT specialist; they’ll assess for polyps or infection. Remember, staying hydrated and avoiding irritants like smoke or strong perfumes helps maintain the delicate balance of your nasal passages. Let’s support each other in keeping our noses healthy.
Neeraj Agarwal November 24, 2025
While the article is generally accurate, there are a few minor inaccuracies that need correction. The term “olfactory epithelium” should be consistently capitalized as a proper anatomical term. Additionally, “sneezing can cause a transient swelling” is better expressed as “sneezing may induce transient mucosal swelling.” Overall, the information is sound, but precision in language is important.
Rose K. Young November 26, 2025
Honestly, this is just basic stuff anyone with a nose could figure out.
Christy Pogue November 27, 2025
Hey everyone! Super excited to see so many helpful tips about keeping our noses in tip‑top shape. I love the suggestion to stay hydrated – I’ll definitely be drinking more water. And those saline rinses? Game changer! Let’s all take care of our sniffers and keep the sneeze‑smell drama at bay. Keep sharing the good vibes!
Helena Pearson November 28, 2025
What a thoughtful piece on the sneezing–smell connection! 🌟 It really highlights how something as simple as a sneeze can have cascading effects on our olfactory health. I especially appreciate the emphasis on simple home remedies like saline irrigation and proper hydration – they’re affordable and effective. It’s also crucial to recognize when professional help is needed, especially with persistent anosmia. Let’s keep spreading awareness and supporting each other in maintaining a healthy sense of smell. 😊
Grover Walters November 29, 2025
From a philosophical standpoint, the sneeze exemplifies the impermanence of sensory experience: a brief, involuntary act that momentarily obscures perception. This aligns with the notion that our senses are contingent upon the delicate equilibrium of physiological processes, which can be disrupted by even the smallest perturbations.
Dominique Watson November 30, 2025
It is evident that understanding the bodily functions, such as sneezing, reinforces the importance of maintaining the health of our national population; therefore, we must prioritize research funding in this area.
Joshua Brown November 30, 2025
Great summary, here are a few additional points to consider: saline nasal irrigation can physically remove irritants, staying well‑hydrated thins mucus, antihistamines can reduce histamine‑mediated sneezing, and consulting an ENT specialist is advisable for chronic issues, especially when symptoms persist beyond two weeks, as prolonged anosmia may indicate underlying pathology.
andrew bigdick December 1, 2025
Thanks for the detailed info; I’d add that keeping the indoor humidity around 40‑50 % can help maintain nasal moisture and support olfactory function.