Understanding Glaucoma and Its Treatment Options
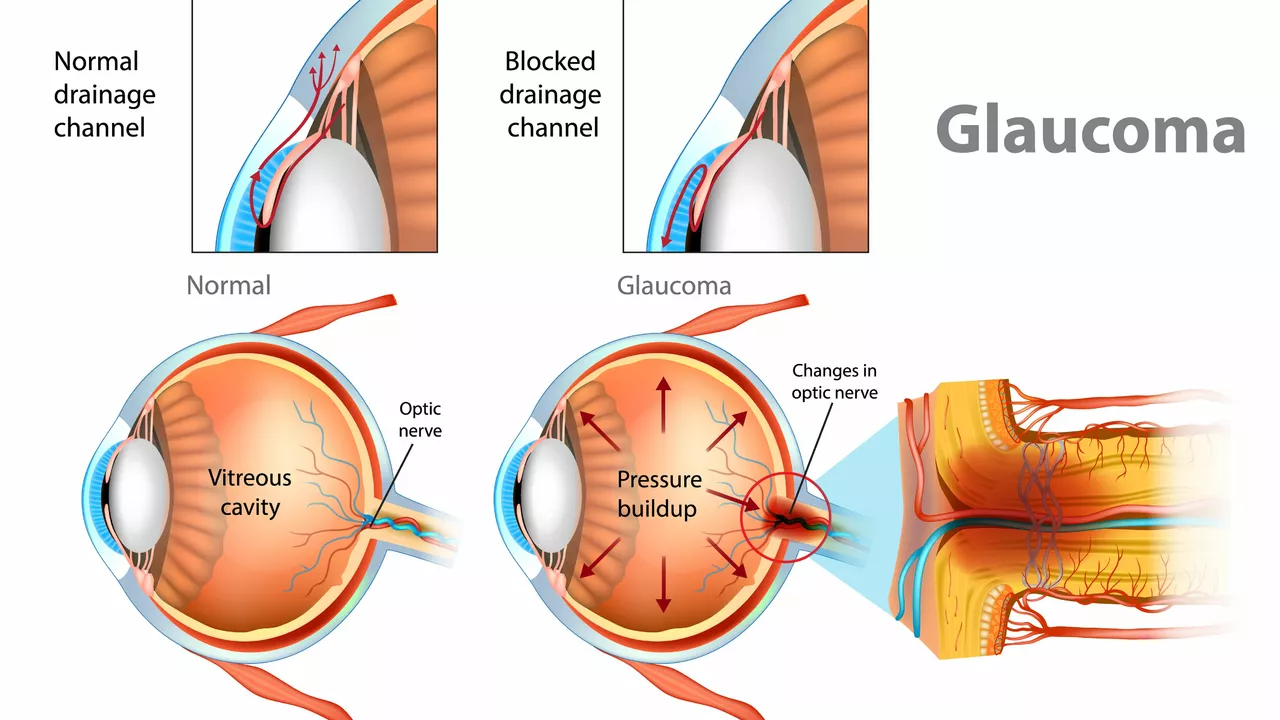
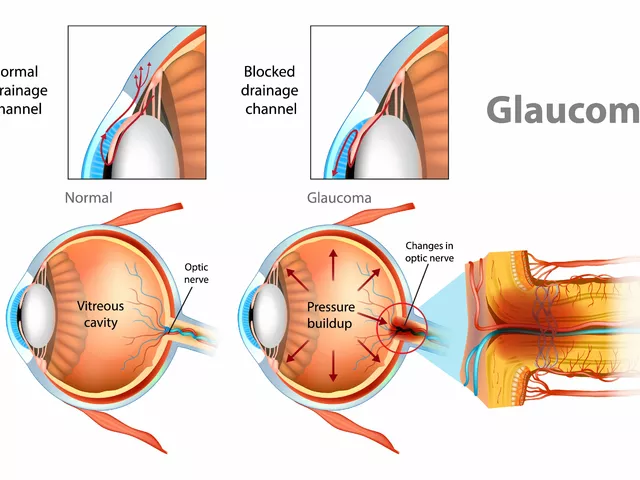
Before we dive into the comparison of acetazolamide and other glaucoma medications, it's important to first understand what glaucoma is and the different treatment options available. Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, often resulting in vision loss and blindness. It's typically caused by abnormally high pressure in your eye and is one of the leading causes of blindness for people over the age of 60. Treatment options range from eye drops to surgery, with medication being a common treatment route.
An Overview of Acetazolamide
Acetazolamide is a medication used primarily in the treatment of glaucoma. It's a type of carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, which works by decreasing the amount of fluid produced in the eyes, thereby reducing eye pressure. Acetazolamide is often prescribed when other medications have not been effective, or in more severe cases of glauoma. It's available in tablet form, and like all medications, it can cause side effects, some of which can be serious. It's also important to note that acetazolamide may not be suitable for everyone, such as those with kidney problems or certain allergies.
Other Glaucoma Medications
While acetazolamide is a commonly prescribed medication for glaucoma, it's not the only one. Other glaucoma medications include prostaglandins, beta blockers, and alpha-adrenergic agonists. Prostaglandins work by increasing the outflow of fluid in the eye to lower eye pressure. Beta blockers, on the other hand, reduce the production of fluid in the eye. Alpha-adrenergic agonists both decrease fluid production and increase fluid outflow. These medications are typically available as eye drops and are usually the first line of treatment for glaucoma.
Comparing Efficacy
When comparing the efficacy of acetazolamide and other glaucoma medications, it's important to remember that different medications work in different ways and the effectiveness can vary from person to person. That said, studies have shown that while prostaglandins and beta blockers are generally more effective than acetazolamide at reducing intraocular pressure, acetazolamide may be more effective in more severe cases of glaucoma or when other treatments have not been effective.
Weighing the Side Effects
Side effects are another important consideration when comparing acetazolamide and other glaucoma medications. Acetazolamide can cause side effects such as nausea, dizziness, and frequent urination. More serious side effects can include kidney stones and metabolic acidosis. Other glaucoma medications also come with their own potential side effects. For example, prostaglandins can cause changes in eye color and eyelash growth, while beta blockers can cause low blood pressure, reduced pulse rate, and fatigue. It's important to discuss these potential side effects with your doctor when deciding on a treatment plan.
Considering Personal Factors
Lastly, personal factors can play a key role in determining which medication is right for you. This can include your overall health, lifestyle, and the severity of your glaucoma. For example, if you have kidney problems, acetazolamide may not be the best choice for you. Or, if you have a very active lifestyle, the frequent urination caused by acetazolamide may be inconvenient. On the other hand, if other treatments have not been effective, or if you have severe glaucoma, acetazolamide may be the most effective option. It's crucial to have a thorough discussion with your doctor to determine the best treatment plan for you.





Arjun Santhosh June 27, 2023
I think the urination thing with acetazolamide can be a real hassle if you're busy, especially when you have to run to the bathroom every few hours.
It's also kinda cheap compared to some of the newer drops, so for folks on a tight budget it might make sense.
Stephanie Jones June 30, 2023
When you stare into the mirror of your own health, you realize that the choice between a pill and a drop is more than a medical decision; it's a quiet dialogue with the self, a subtle surrender to the rhythms of your body.
Nathan Hamer July 3, 2023
Acetazolamide, a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, steps onto the stage of glaucoma management like an under‑dog with a hidden spark! 🌟 Its oral form gives it an edge when patients struggle with drop compliance, especially in severe cases where intra‑ocular pressure spikes wildly.
Yet, the very mechanism that drains fluid can also drain your electrolytes, leading to metabolic acidosis if not monitored carefully.
Prostaglandin analogues, on the other hand, work by increasing outflow through the uveoscleral pathway, often delivering a steadier pressure reduction in milder disease.
Beta‑blockers cut production at the source, but they bring the risk of systemic cardiovascular effects that can be problematic for older patients with heart issues.
Alpha‑adrenergic agonists try to do both – reduce production and increase outflow – but they can cause ocular surface irritation that many find intolerable.
Side‑effect profiles differ dramatically: acetazolamide may cause frequent urination, tingling sensations, and rare kidney stones, while prostaglandins can change iris color and lash length.
Patients with renal impairment should steer clear of acetazolamide, making the topical options more attractive.
If you’re an athlete or traveler, the diuretic effect of acetazolamide could be a nuisance, potentially disrupting hydration strategies.
Conversely, those with asthma may find beta‑blockers unsuitable, nudging the choice toward oral therapy or prostaglandin drops.
Clinical trials have shown that prostaglandins often achieve a greater average IOP drop than acetazolamide, but the latter shines when other meds fail or when rapid pressure control is needed.
Cost considerations also matter; generic acetazolamide tablets are generally cheaper than many branded eye drops, an important factor for those without robust insurance.
Adherence is a hidden hero: a once‑daily oral pill may be easier for some than multiple daily drop instillations, yet forgetfulness can still strike.
Ultimately, the decision hinges on individual health status, comorbidities, lifestyle, and how a patient tolerates side effects.
Discussing these nuances with an ophthalmologist ensures the therapy aligns with the person’s overall well‑being. 😊
Tom Smith July 6, 2023
Sure, because drinking more water to offset frequent urination is exactly what everyone wants.
Kyah Chan July 9, 2023
From a pharmacoeconomic perspective, the cost‑effectiveness ratio of acetazolamide versus prostaglandin analogues merits rigorous scrutiny. While the oral formulation is inexpensive, its systemic adverse event profile can precipitate ancillary healthcare expenditures. Conversely, prostaglandin eye drops, albeit pricier per unit, demonstrate superior adherence and marginally better intra‑ocular pressure reduction in randomized controlled trials. The clinician must weigh direct drug costs against indirect costs arising from monitoring, adverse event management, and potential loss of productivity. In populations with limited renal function, the contraindication of acetazolamide further tilts the balance toward topical agents. Therefore, a stratified approach based on comorbidity indices and socioeconomic status is advisable.
Ira Andani Agustianingrum July 12, 2023
Hey, just wanted to say you don’t have to pick one thing and stick with it forever. If the drops start messing with your eyes or you feel weird on the pill, chat with your doc and switch it up. Sometimes a combo works best – a low‑dose tablet plus a drop can keep the pressure down without major side effects. Keep track of how you feel and share that info; it helps the doctor find the sweet spot. Remember, your comfort matters as much as the numbers.
James Higdon July 15, 2023
It is morally incumbent upon healthcare providers to prioritize patient safety over pharmaceutical profit motives.
Wanda Smith July 18, 2023
Ever wonder why big pharma pushes eye drops so hard? They keep the profit wheels turning while we swallow pills that actually get to work systemically. The whole system is rigged to keep us dependent on expensive, brand‑name topicals.
Bridget Jonesberg July 21, 2023
One cannot help but observe that the discourse surrounding glaucoma therapeutics often suffers from a regrettable paucity of nuance, wherein the binary opposition of oral versus topical agents is presented as a simplistic dichotomy, thereby obscuring the intricate pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic interplays that undergird therapeutic decision‑making. Moreover, the sociocultural determinants of patient adherence, the economic stratifications influencing drug accessibility, and the idiosyncratic physiological responses to carbonic anhydrase inhibition versus prostaglandin analogues demand a more erudite contemplation than is typically afforded in mainstream dialogues.
Marvin Powers July 23, 2023
Oh, the drama of choosing a pill over a drop! It's like picking between a reliable sedan and a flashy sports car-both will get you to the same destination, but one might make you feel cooler while the other just gets the job done without all the fuss. If you love the convenience of a single daily tablet and don't mind the occasional bathroom sprint, acetazolamide could be your trusty sedan. But if you prefer a drop that works locally and keeps potential systemic side effects at bay, the prostaglandin drops are your sleek convertible-sure, you have to remember the morning routine, but the ride is smoother. Bottom line: weigh the pros, consider your lifestyle, and let your eye doctor be the co‑pilot.
Jaime Torres July 26, 2023
Nice summary.
Wayne Adler July 29, 2023
Look, if you ignore the risk of kidney stones you’re just being reckless. Acetazolamide isn’t a magic bullet; you gotta monitor labs, stay hydrated, or you’ll end up in trouble.
Shane Hall August 1, 2023
Great points! Adding to that, the ocular surface irritation from alpha‑agonists can really affect quality of life, so it’s worth discussing alternatives early on. Also, consider patient education on proper drop technique to maximize efficacy.
Christopher Montenegro August 4, 2023
From a mechanistic standpoint, the pharmacodynamic profile of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors involves inhibition of aqueous humor synthesis via enzymatic blockade, which, while clinically effective, introduces systemic acid‑base disturbances that must be quantified through arterial blood gas monitoring. In contrast, prostaglandin receptor agonists modulate uveoscleral outflow, offering a more targeted approach with a distinct side‑effect spectrum including melanocytic activation. The differential risk‑benefit calculus mandates a precision‑medicine framework, integrating renal function indices and cardiovascular comorbidities into therapeutic algorithms.
Kyle Olsen August 7, 2023
Honestly, the only reason anyone would even consider acetazolamide these days is because they haven't kept up with the latest guidelines. The evidence is clear: prostaglandin analogues dominate in efficacy and safety.
Sarah Kherbouche August 10, 2023
Sure, let’s all trust big pharma’s “research” while they keep pricing eye drops sky‑high. They’ll tell you oral meds are risky, but it’s just a ploy to keep you buying their overpriced drops.
MANAS MISHRA August 13, 2023
Arjun, good point about cost. I’d add that checking kidney function before starting acetazolamide is essential, especially for patients with pre‑existing renal issues.
Lawrence Bergfeld August 16, 2023
James, agreeing-choose wisely; consider both efficacy and side‑effects!;.