Clinical Pharmacology: Understanding How Drugs Work in the Body
When you take a pill, it doesn’t just disappear—it goes through a complex journey inside your body. This is where clinical pharmacology, the science of how drugs interact with the human body to produce effects, both therapeutic and harmful. Also known as drug action science, it’s the bridge between lab research and what actually happens when you swallow a tablet or get an injection. It answers questions like: Why does this drug make me drowsy? Why does it work for my friend but not me? And why do some meds need to be taken on an empty stomach?
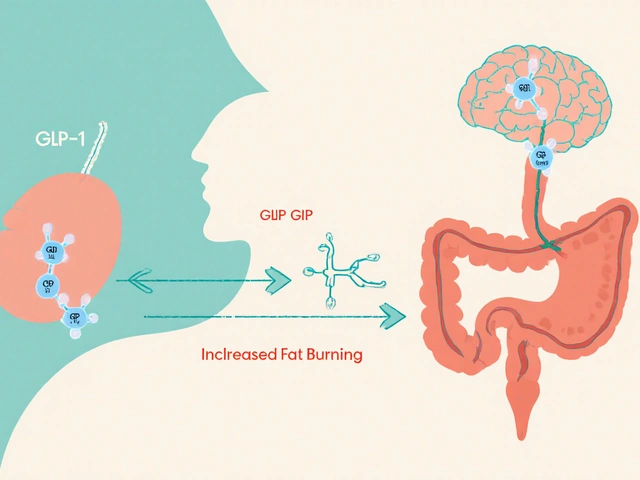
Clinical pharmacology isn’t just about what a drug does—it’s about how your body changes the drug. That’s pharmacokinetics, how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and excretes a medication. Think of it like a delivery system: How fast does the drug reach your bloodstream? Does your liver break it down too quickly? Does it build up if you have kidney problems? These details matter. A dose that’s safe for one person could be dangerous for another because of age, weight, genetics, or other meds they’re taking. That’s where drug interactions, when one medication changes how another works in the body. come in. Take warfarin and ibuprofen together? That can raise bleeding risk. Mix fentanyl patches with alcohol? That’s a life-threatening combo. These aren’t hypotheticals—they’re real risks documented in studies and patient reports.
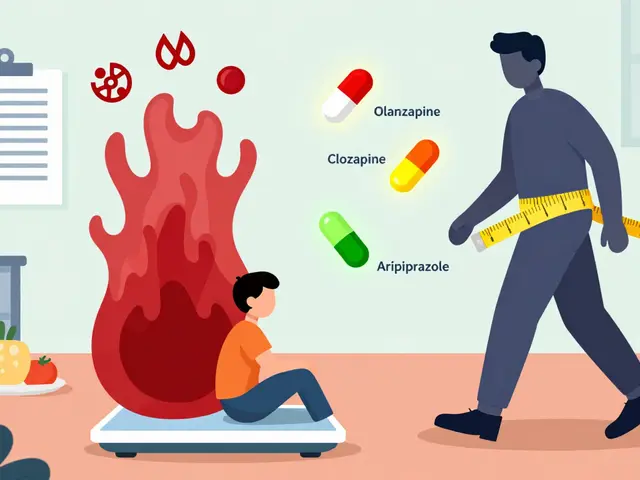
And then there’s the flip side: adverse drug reactions, unintended, harmful effects that happen even when a drug is taken correctly. Some show up fast—like a rash or trouble breathing. Others creep in slowly, like liver damage from long-term acetaminophen use or kidney stress from NSAIDs. The posts here don’t just list side effects—they explain why they happen, who’s most at risk, and what to do next. You’ll find real-world breakdowns of black box warnings, how fiber supplements can block absorption, why certain painkillers are risky with high blood pressure meds, and how insulin biosimilars compare to brand-name versions in actual use.
This isn’t theory. It’s what pharmacists and doctors use every day to decide if a drug is right for you. Whether you’re managing gout, switching antidepressants, dealing with opioid constipation, or trying to understand why your hormone therapy needs monitoring, clinical pharmacology gives you the tools to ask better questions and spot red flags before they become emergencies. Below, you’ll find clear, no-fluff guides on the most common—and most dangerous—medication issues people face. No jargon. Just what you need to know to stay safe and informed.
How to Read Drug Interaction Tables in FDA Labels Like a Pro
Learn how to read FDA drug interaction tables to prevent dangerous medication combinations. Understand Section 7, Section 2, and Section 12 to make safer prescribing decisions.