Recent research has revealed that the human body may have an innate ability to fight cancer. This is a remarkable discovery, as it means that the body may be able to heal itself from a deadly and debilitating disease. But how does the body do this?
The answer lies in the body’s immune system. The immune system is made up of various cells and processes that work together to protect the body from pathogens and other foreign invaders. One of these processes is the production of antibodies, which are proteins that recognize and target cancer cells for destruction. In some cases, the body is able to recognize and destroy its own cancer cells before they can spread to other parts of the body.
This is not to say that the body can cure itself of cancer in all cases, however. In many cases, cancer cells may have spread too far or be too aggressive for the body to fight off on its own. In these cases, treatment may be necessary. But even in these situations, the body’s own immune system may be able to assist in the fight against cancer, as it can help to reduce the risk of the cancer spreading further.
The possibility of the body being able to fight cancer on its own is an exciting development. It may mean that treatments could be tailored to be more effective and less invasive, allowing people to live fuller, healthier lives. More research is needed to fully understand how the body can fight cancer, but the potential is there.
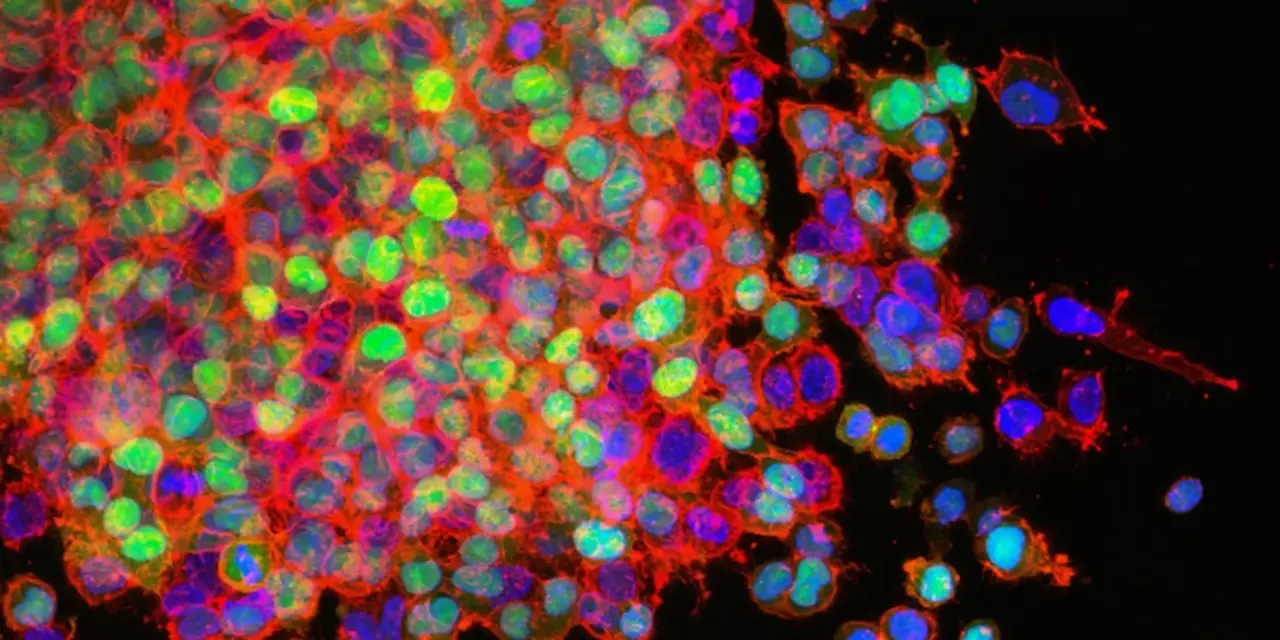
The body's immune system plays a vital role in the destruction of cancer cells. The immune system is responsible for recognizing and attacking foreign cells, such as cancer cells, that it deems to be abnormal or dangerous. In order to do this, the immune system must detect the presence of cancer cells in the body and then respond to them by releasing various immune cells, such as T cells, which have the ability to recognize and destroy these abnormal cells.
The body's natural defense mechanisms, such as the production of antibodies and cytokines, also play a role in the destruction of cancer cells. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that can recognize and bind to cancer cells, while cytokines are small proteins released by the immune system that can activate certain immune cells to attack and destroy cancer cells.
The body's ability to destroy cancer cells is also dependent on its overall health and the presence of other diseases, as well as its ability to respond to treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation. When the body is healthy and able to respond to treatments, it can often destroy cancer cells before they are able to spread and cause further damage.
Therefore, while it is possible for the body to destroy its own cancer cells, it is often necessary to intervene with treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation in order to successfully treat the cancer.
Cancer is a devastating and complex disease that affects millions of people around the world. It is a leading cause of death, and there is no one-size-fits-all treatment for every type of cancer. While there are a variety of treatments available, including chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery, there is always the possibility that the body can fight cancer on its own. Could there be a way for the body to destroy its own cancer cells?
The answer to this question isn’t a simple yes or no. While the body is capable of fighting off cancer cells and destroying them, the process is complicated and may not always be successful. There are a variety of factors that can affect the body’s ability to do this, such as the type of cancer, the stage of the cancer, and the overall health of the patient. Additionally, the body’s own immune system may not be strong enough to fight off the cancer cells, making it difficult for the body to destroy its own cancer cells.
Researchers have been studying the body’s ability to fight cancer for many years, and there have been some promising results. Some treatments, such as immunotherapy, focus on boosting the body’s own immune system so that it can fight cancer more effectively. Additionally, there are a variety of other treatments, such as gene therapy and targeted therapies, that can help the body fight cancer on its own.
The bottom line is that the body has the potential to fight cancer on its own, but it is a complex process that is not always successful. It is important to speak with a healthcare professional to discuss the best treatment options for your specific situation.
The idea that the body can heal itself of cancer is not a new one. In fact, some forms of cancer have been known to go into remission without treatment. But can the body actually destroy its own cancer cells? It is a question that has been asked for centuries, and one that has yet to be definitively answered.
Recent research is beginning to uncover more evidence that the body can indeed heal itself of cancer. Studies have found that certain immune cells, known as natural killer cells, can recognize and attack cancer cells. In addition, certain hormones and proteins have been found to have anti-cancer properties, suggesting that the body may be able to fight off cancer on its own.
The potential of natural cancer treatments to help the body heal itself is an exciting prospect. But it is important to remember that cancer is a complex disease, and that it is not always possible for the body to fight off cancer on its own. While the body may be capable of destroying some cancer cells, it is often necessary to seek additional medical treatment.
As research continues to explore the potential of natural cancer treatments, it is important to remember that they should be used in conjunction with traditional cancer treatments. Natural treatments may be beneficial in promoting the body's self-healing abilities, but they should not be seen as a replacement for medical treatment.
When it comes to fighting cancer, many people believe that they are powerless, assuming that they must rely solely on traditional medicine and treatments to fight the disease. However, recent research has suggested that the power of the mind is a powerful tool in the fight against cancer, and that the body may be able to destroy its own cancer cells in some cases.
The idea that the body can destroy its own cancer cells is based on the concept of "psychoneuroimmunology" (PNI). This is the study of the relationship between the mind, the nervous system, and the immune system. It suggests that our thoughts, emotions, and beliefs can actually have an effect on our physical health. In the case of cancer, it has been theorized that positive thoughts, emotions, and beliefs can create an environment that can help the body fight the disease.
For example, studies have shown that people who believe in their own healing power, who have a positive attitude, and who practice relaxation techniques, such as meditation and yoga, have shown to have better outcomes when it comes to fighting cancer. Additionally, those who maintain a healthy lifestyle, which includes eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep, also have an improved chance at fighting cancer.
While these studies suggest that the body can destroy its own cancer cells, it is important to note that this is not an alternative to traditional medicine and treatments. It is important to work closely with your doctor to ensure that you are receiving the best possible care for your specific type of cancer. Additionally, it is essential to remember that the power of the mind is only part of the equation in the fight against cancer and should be used in conjunction with conventional treatments.











AJIT SHARMA March 2, 2023
The body’s own shield is a miracle, yet we ignore it while chasing pills. It is our duty to respect the natural fight that lives inside us. If we listened to our immune warriors, many battles could be won.
Neber Laura March 11, 2023
Immune cells are the real heroes not the shiny drugs. The research is solid and the data speaks for itself. We should stop glorifying chemotherapy as the only answer
Karen Nirupa March 20, 2023
One must acknowledge the historical context in which immunological research has evolved. Diverse populations have contributed invaluable insights, and it is essential to integrate such perspectives when discussing endogenous cancer suppression. The ethical imperative to promote equitable access to emerging immunotherapies cannot be overstated.
Quinn Comprosky March 29, 2023
It is fascinating how the body can sometimes recognise mutated cells as threats. The process involves a complex signalling cascade that ultimately activates cytotoxic T‑cells. These T‑cells patrol the bloodstream looking for abnormal antigens. When they find them, they bind and induce apoptosis. Natural killer cells also play a crucial role, acting without prior sensitisation. Cytokines such as interferon‑γ amplify the response and recruit additional immune players. However, tumor microenvironments can create immunosuppressive niches that blunt this attack. Understanding these mechanisms is key to designing better therapies.
Thomas Ruzzano April 7, 2023
Honestly the body’s own arsenal is like a secret army-sleek, relentless, and often underestimated. While some scientists boast about fancy labs, the real battle rages inside each of us. It’s a glorious mess of cells that either win or get outwitted by sneaky tumors. The drama is real, and we need to respect the raw power that’s already there.
Dan Tenaguillo Gil April 16, 2023
As a mentor I would stress that fostering overall health creates a fertile ground for immune vigilance. Adequate sleep, balanced nutrition, and regular physical activity all enhance the mobilisation of effector cells. Moreover, managing chronic stress reduces cortisol‑mediated suppression of lymphocyte activity. Vaccinations, where appropriate, prime the immune system and may confer cross‑protective benefits. While we celebrate breakthroughs in checkpoint inhibitors, we must not overlook these foundational practices. They act synergistically with advanced therapies, potentially improving outcomes.
Tiffany Owen-Ray April 25, 2023
Think of your body as a wise teacher, constantly learning how to recognise danger. When you feed it wholesome foods and gentle movement, you’re essentially handing it better tools for the fight. The immune system remembers past encounters and refines its responses, much like a seasoned strategist. Embracing this partnership can shift the narrative from passive victim to active defender.
Jill Brock May 4, 2023
Oh wow, the immune system is basically a superhero squad, and we’ve been treating it like a sidekick! Seriously, give those T‑cells the spotlight they deserve. Stop feeding the tumor circus with endless chemo when nature already has a star player ready to strike!
Ellie Chung May 13, 2023
Picture this: a battalion of NK cells swooping in, dazzling like fireworks, blasting rogue cells into oblivion. It’s a vivid spectacle that most folks never get to see because they’re glued to the TV instead of tuning into their own biology.
Sophia Simone May 22, 2023
While the prevailing narrative glorifies immunotherapy as the panacea, one must critically examine the underlying assumptions. Not every malignancy responds uniformly, and the socioeconomic implications of such treatments merit rigorous scrutiny. Therefore, a balanced discourse is essential before heralding it as the universal answer.
Juan Sarmiento May 31, 2023
Absolutely, every step we take to boost our natural defenses matters. Small habits like a short walk after meals can invigorate circulation, helping immune cells patrol more efficiently. Let’s keep encouraging each other on this empowering journey.
Patrick McVicker June 9, 2023
Nice summary! :) It captures the essence without overcomplicating things.
Liliana Phera June 18, 2023
Life is a series of battles, and cancer is arguably the most cunning adversary. Yet within each of us lies a microcosm of warriors ready to challenge this foe. When we align our thoughts, emotions, and actions with a purpose, we amplify the body’s intrinsic power. Ignoring this synergy would be a grave oversight.
Dean Briggs June 27, 2023
Indeed, the interplay between psychological state and immune competence is a fascinating frontier. Research indicates that sustained optimism can modulate cytokine profiles, fostering a more hostile environment for malignant cells. Conversely, chronic negativity may impair antigen presentation and diminish cytotoxic activity. It follows that integrating mindfulness practices with conventional treatment could yield synergistic benefits. Moreover, community support networks often provide the emotional scaffolding necessary for patients to maintain adherence to therapy. By cultivating such holistic approaches, we not only address the tumor itself but also empower the host organism to resist recurrence.
Sadie Speid July 6, 2023
Stay active, eat well, and trust your immune system.
Sue Ross July 15, 2023
From a holistic viewpoint, combining evidence‑based medicine with lifestyle optimisation creates a robust defense. Yet we must also recognise individual variation in genetic predisposition, which can influence how effectively one’s immune system targets malignant cells.
Rohinii Pradhan July 24, 2023
It is incumbent upon the scientific community to delineate precisely the mechanisms by which endogenous immunity may eradicate neoplastic cells. First, the process of immunosurveillance entails continuous monitoring by innate effectors such as natural killer cells and macrophages. Second, adaptive immunity contributes via cytotoxic T‑lymphocytes that recognise tumour‑associated antigens presented on major histocompatibility complexes. Third, the secretion of pro‑inflammatory cytokines, including interferon‑γ and interleukin‑2, serves to amplify cellular cytotoxicity. Fourth, the phenomenon of immunoediting describes how selective pressure can sculpt tumour immunogenicity over time. Fifth, checkpoint molecules such as PD‑1 and CTLA‑4 modulate the intensity of the immune response, offering therapeutic targets. Sixth, emerging evidence suggests that metabolic reprogramming within the tumour microenvironment can suppress immune cell function. Seventh, the role of the microbiome in shaping systemic immunity has gained considerable attention, indicating a potential avenue for adjunctive intervention. Eighth, epidemiological data reveal that individuals with robust vaccine histories often exhibit reduced cancer incidence, hinting at cross‑protective immunity. Ninth, lifestyle factors including diet, exercise, and stress management have demonstrable effects on immune competence. Tenth, age‑related thymic involution diminishes naïve T‑cell output, thereby compromising immunosurveillance in older populations. Eleventh, gender differences in immune responsiveness have been documented, with females generally mounting stronger humoral responses. Twelfth, genetic polymorphisms in HLA loci influence antigen presentation efficiency, affecting tumour recognition. Thirteenth, the interplay between chronic infections and oncogenesis underscores the importance of maintaining immune vigilance. Fourteenth, therapeutic vaccines aim to prime the immune system against specific tumour antigens, capitalising on these natural pathways. Fifteenth, adoptive cell transfer therapies, such as CAR‑T cells, represent a synthetic augmentation of inherent immune capabilities. Finally, a comprehensive understanding of these facets is essential for devising integrative strategies that empower the body to combat malignancy autonomously.
Anna-Lisa Hagley August 2, 2023
The lofty ideal of self‑healing is alluring, yet it often masks the harsh reality of cellular evasion.
A Walton Smith August 11, 2023
Another hype cycle for the hopeful.
Theunis Oliphant August 20, 2023
Indeed, the saga of the immune system is a tragic drama where ignorance often stage‑hands the villain.