Foreign Manufacturing: What It Means for Your Medications and Safety
When you pick up a pill bottle, chances are the active ingredient inside was made somewhere else—often in countries like India or China. This is foreign manufacturing, the production of pharmaceutical ingredients or finished drugs outside the country where they’re sold. Also known as global drug production, it’s how most generic medications stay affordable, but it also raises real questions about oversight and quality. The U.S. FDA inspects foreign factories, but only a fraction get checked each year. That means your blood pressure pill, your antibiotic, or your insulin might have traveled thousands of miles before reaching your medicine cabinet.
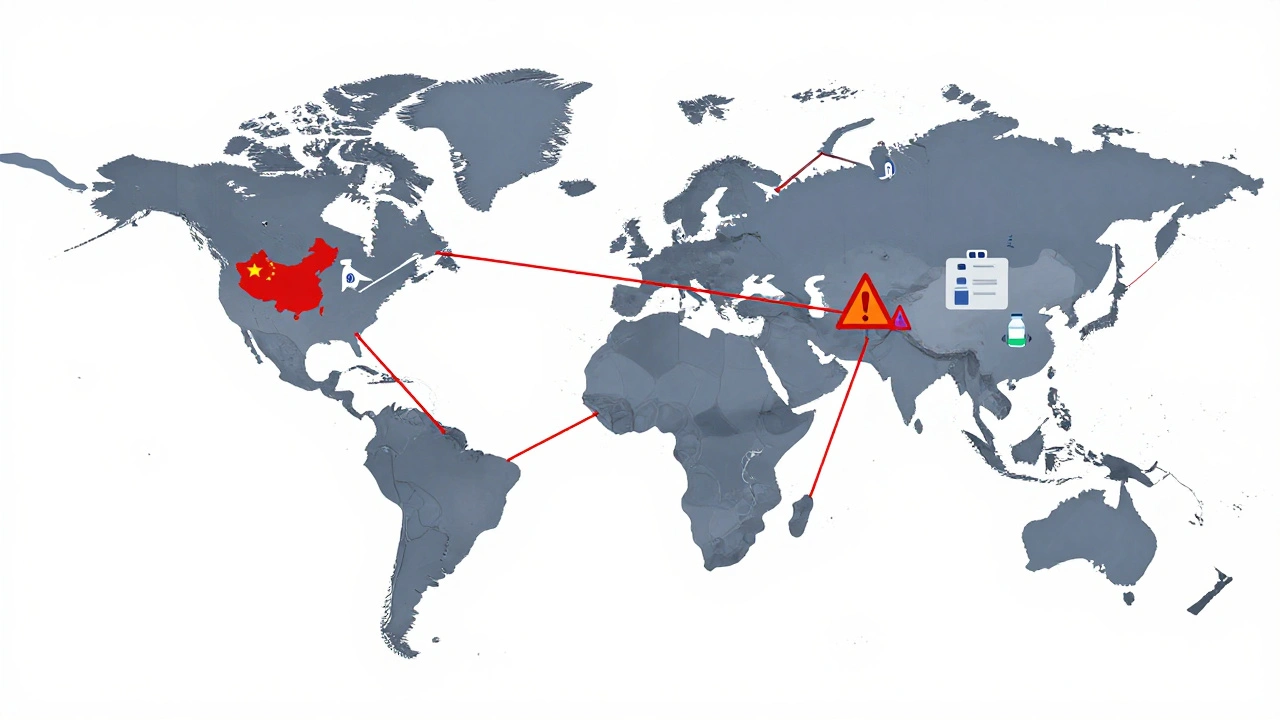
That’s not inherently bad. Many foreign facilities meet or exceed U.S. standards. In fact, over 80% of the active ingredients in U.S. medicines come from abroad. But it does mean drug safety, the system that ensures medications work as intended without harmful side effects depends heavily on international supply chains. A single factory in India can supply thousands of U.S. pharmacies with metformin or lisinopril. If something goes wrong there—a contamination, a data造假, a skipped quality test—it doesn’t just affect one batch. It affects everyone who takes that drug.
That’s why pharmaceutical supply chain, the network of manufacturers, distributors, and regulators that move drugs from factory to patient matters more than ever. It’s not just about shipping containers and customs forms. It’s about traceability. It’s about knowing if the raw material in your medication was tested properly, stored correctly, and handled by trained workers. The FDA regulations, the rules enforced by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to ensure drug quality and safety are strict on paper, but enforcement happens overseas, where language, culture, and local practices can create blind spots.
What you’ll find in this collection isn’t a rant about outsourcing. It’s a clear-eyed look at how foreign manufacturing touches your health. You’ll see how the foreign manufacturing system enables low-cost generics that millions rely on—while also creating risks that aren’t always visible. You’ll learn how the FDA’s Orange Book tells you which generics are approved, how MedWatch catches safety issues that slip through, and why black box warnings sometimes trace back to a factory halfway across the world. You’ll also find real examples: how a contamination in a foreign plant led to a nationwide recall, how supply chain delays caused life-threatening shortages, and why some patients notice subtle differences in generic versions.
These aren’t theoretical concerns. They’re everyday realities. Whether you’re on insulin, a mood stabilizer, or a simple pain reliever, the drug in your hand likely came from a facility you’ve never seen, governed by rules you may not know. This collection gives you the tools to understand that system—not to fear it, but to use it wisely. You’ll learn how to check if your medication is FDA-approved, how to report side effects that might point to a manufacturing issue, and why your pharmacist’s advice on generic switches matters more than you think. The next time you fill a prescription, you’ll know exactly what’s behind the label—and what you can do to protect yourself.
International Supply Chains: Why Foreign Manufacturing Is Causing Drug Shortages in 2025
International supply chains for pharmaceuticals are under strain, causing widespread drug shortages in 2025. Over 80% of active ingredients come from China and India, making the system vulnerable to disruptions. Here’s how it’s happening-and what’s being done to fix it.