Metastasis: Understanding Cancer Spread
When cancer spreads from its original spot to other parts of the body, that’s called metastasis. It’s a big deal because it can change how doctors treat the disease and what kind of outlook patients can expect. But what exactly happens during metastasis? And why is it so important to catch it early? Here’s the lowdown in clear terms.
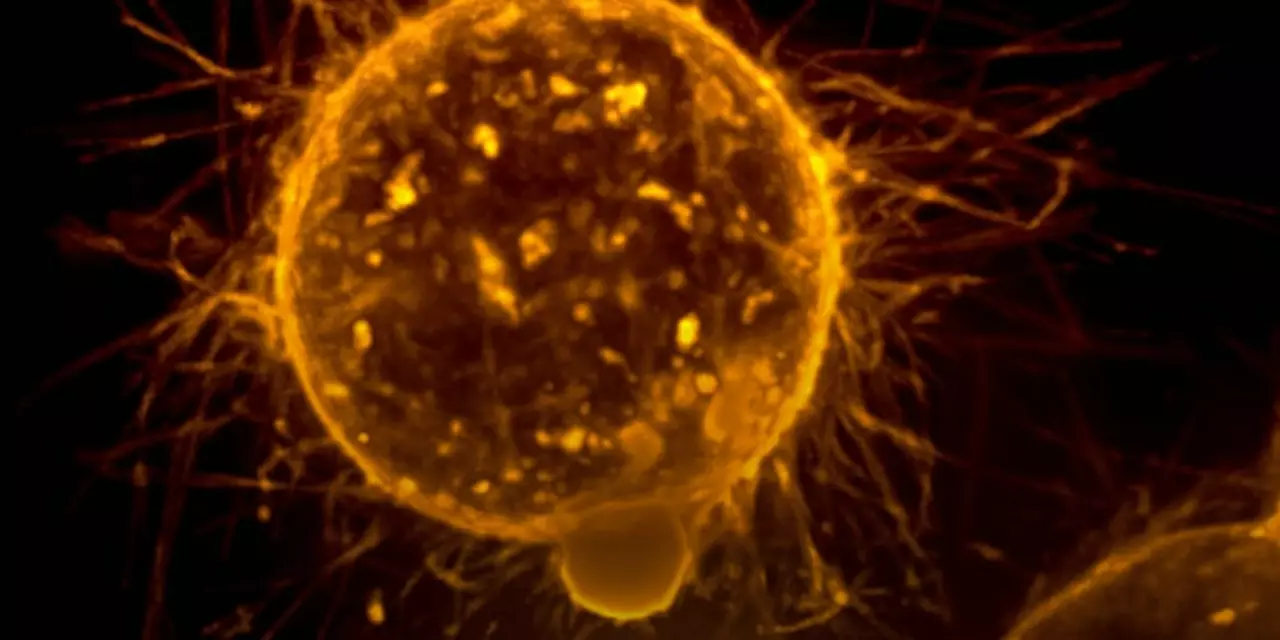
At its core, metastasis means cancer cells break away from the initial tumor, travel through the bloodstream or lymph system, and settle somewhere new. Think of it like seeds being carried by the wind to grow in different fields. Those seeds can start new tumors, which might behave differently than the original one.
Common Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Not all metastatic cancer causes obvious symptoms right away, but some clues might include unexplained weight loss, persistent pain, or new lumps under the skin. Sometimes people feel tired or notice organ-related issues, depending on where the cancer travels. If you notice anything unusual or persistent, let your doctor know—early detection can make a big difference.
Why Metastasis Changes Treatment Plans
Having cancer spread means doctors often need to rethink treatment. The goal might shift from curing the disease to controlling it and maintaining quality of life. Treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy might be used based on where the cancer has spread and how it’s behaving. It’s worth keeping in mind that many people with metastatic cancer live well with the right care.
Understanding metastasis helps you stay informed and empowered. It’s not just a scary word—knowing what it means can lead to earlier action and better conversations with your healthcare team. If you or a loved one is facing this, ask questions, get the facts, and remember that support and options are available.
What is metastatic prostate cancer?
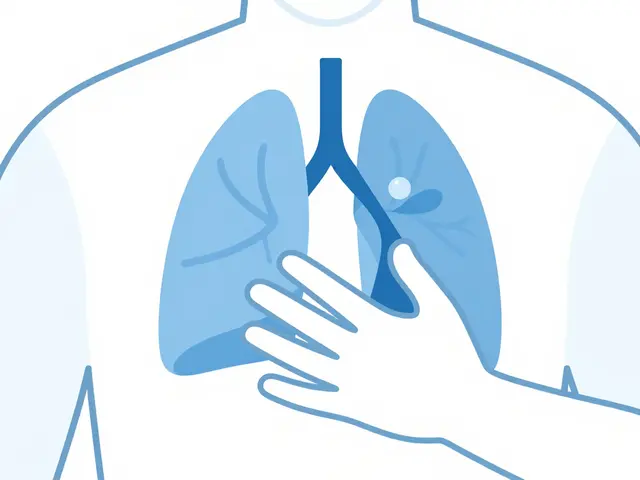
Metastatic prostate cancer is a type of advanced prostate cancer where the cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body. It is the most serious form of prostate cancer, as it is incurable and can be fatal. Common sites of metastasis are the bones, lymph nodes, and lungs. Symptoms vary depending on the location of the spread and may include pain, difficulty urinating, and weight loss. Treatment options include hormone therapy, chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery. Early detection and treatment are key to managing metastatic prostate cancer.
Why are flat cells more likely to become metastatic?
Flat cells, or squamous cells, are more likely to become metastatic than cuboidal cells. This is due to the fact that flat cells have a greater surface area to volume ratio. This means that they have a greater ability to absorb nutrients, which allows them to proliferate and spread more quickly than cuboidal cells. Additionally, flat cells are more likely to attach to surfaces, which helps them to spread more easily. Finally, flat cells are more likely to form protrusions, which helps them to penetrate barriers and migrate more easily.