SSRI Alternatives – Your Quick Reference Guide
When exploring SSRI alternatives, non‑SSRI options for treating depression and anxietynon‑SSRI antidepressants, it's helpful to see how they stack up against traditional antidepressants, medications that adjust brain chemistry to lift mood. Many people start on SSRIs but run into side‑effects or inadequate relief, so they look for a different pathway. Below you’ll find a plain‑talk rundown that connects the dots between each class, their typical uses, and what to watch out for.
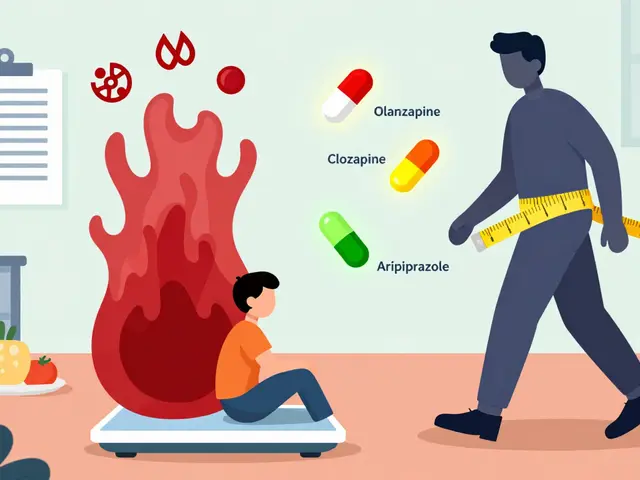
One of the biggest reasons patients switch is the side‑effect profile. SSRIs can cause nausea, sleep trouble, or sexual dysfunction, which can sap motivation to stay on treatment. That’s where SNRI, drugs that boost both serotonin and norepinephrine levels step in. By hitting two neurotransmitters, SNRIs often provide stronger pain relief and less sexual side‑effects, making them a popular second line. Understanding this shift highlights the semantic triple: "SSRI alternatives encompass SNRI options".
SNRIs such as venlafaxine and duloxetine are the flagship members of this group. Their key attribute is dual reuptake inhibition, which translates into better coverage for mixed mood‑pain syndromes. Typical onset is a bit slower than SSRIs—around two to four weeks—but many users report steadier energy once the drug kicks in. Pricing varies, with generics usually under $30 a month in the U.S., and online pharmacies often list them at a discount. If you’re weighing cost against benefit, SNRIs often land in the sweet spot for insurers.
Another major branch is the tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), a class discovered decades ago but still relevant. TCAs like amitriptyline and nortriptyline block the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine while also affecting histamine and acetylcholine receptors. This broader activity can be a double‑edged sword: it yields strong mood lift and helps with chronic pain, yet it also raises the risk of dry mouth, constipation, and heart rhythm changes. Because of these cardiac concerns, doctors usually reserve TCAs for patients without heart disease and monitor ECGs regularly. This illustrates the triple: "Choosing an SSRI alternative requires understanding pharmacodynamics".
Atypical antidepressants bring yet another twist. Bupropion, for example, targets dopamine and norepinephrine instead of serotonin, which means it often avoids the sexual side‑effects that plague SSRIs and SNRIs. Mirtazapine works by blocking certain serotonin receptors while increasing overall serotonin release, making it useful for patients who struggle with insomnia or weight loss. Both drugs sit under the umbrella of non‑SSRI agents, expanding the toolbox for clinicians. Their distinct mechanisms show how "Side‑effect profile influences selection of alternatives".
Practical factors go beyond chemistry. Insurance coverage, drug interactions, and personal health history shape the final pick. For instance, bupropion is contraindicated with seizure disorders, while SNRIs can raise blood pressure in susceptible individuals. Checking liver and kidney function before starting any new antidepressant is a smart move, especially with older drugs like TCAs that rely on metabolism. Online pharmacy guides can help you compare prices, but always verify the pharmacy’s license and look for a pharmacist‑reviewed certification.
Measuring effectiveness is straightforward: most clinicians use the PHQ‑9 questionnaire at baseline and after four weeks. A drop of five points usually signals a clinically meaningful response. Speed of onset matters too; SNRIs and atypicals might need a bit longer, while TCAs can show benefits sooner but require careful titration. When you line up these metrics with side‑effect risk, you get a clear decision framework that many of the articles below follow.
What You’ll Find Below
This collection gathers detailed comparisons, safety tips, and buying guides for each major SSRI alternative. You’ll see side‑by‑side tables that break down cost, common side effects, and typical dosing. There are step‑by‑step instructions for purchasing cheap generic versions safely, plus checklists to verify a pharmacy’s legitimacy. Whether you’re a patient looking for a smoother experience or a caregiver hunting for a cost‑effective option, the posts ahead give you the facts you need without the jargon.
Ready to dive deeper? Below are the curated articles that walk you through each alternative, from SNRIs to TCAs, with real‑world advice on choosing, buying, and using them safely.
Paroxetine vs. Other Antidepressants: Detailed Comparison and Alternatives
A detailed comparison of Paroxetine with sertraline, fluoxetine, escitalopram, venlafaxine, and bupropion, covering mechanisms, side effects, withdrawal, and best-use scenarios.