Budecort inhaler – essential guide
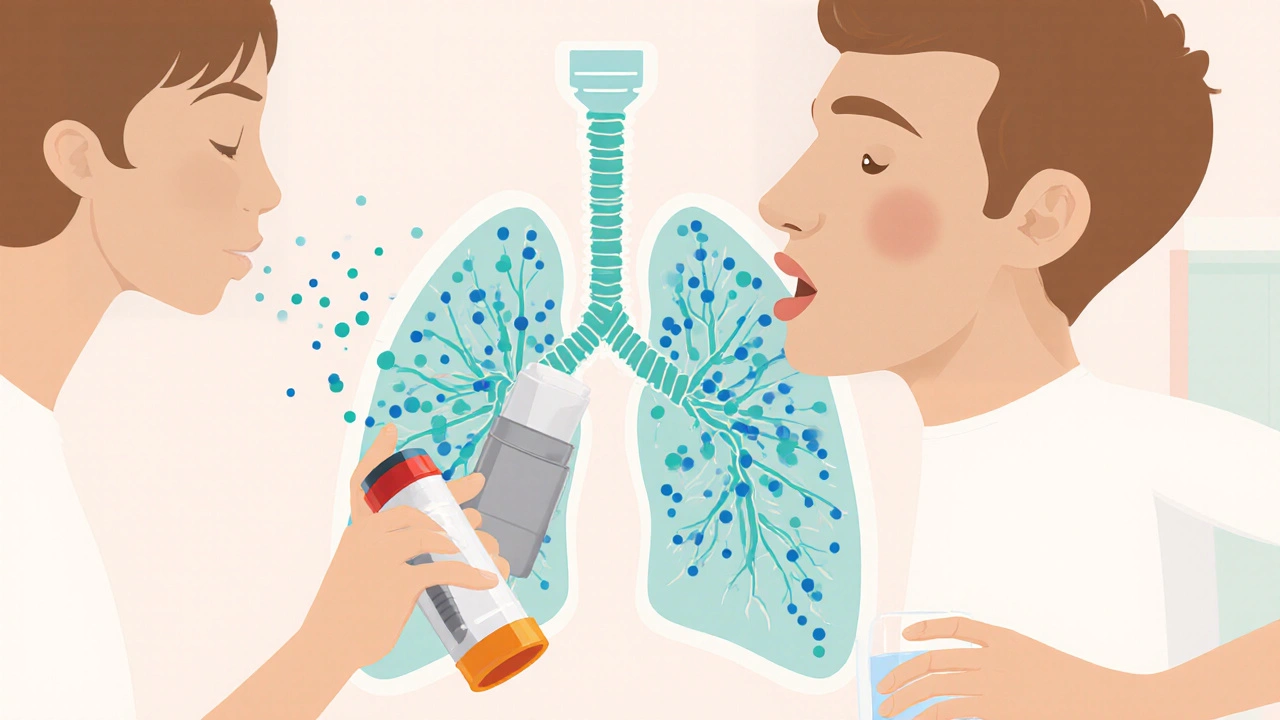
The Budecort inhaler is a press‑air device that delivers the corticosteroid budesonide directly to the lungs. When working with Budecort inhaler, a metered‑dose inhaler designed for chronic respiratory disease. Also known as Budesonide inhalation spray, it belongs to the class of inhaled corticosteroids, which are the cornerstone therapy for airway inflammation. The active ingredient, budesonide, is a synthetic glucocorticoid that binds to intracellular receptors and suppresses the release of inflammatory mediators. Because it targets asthma and COPD, it helps patients avoid flare‑ups, improve lung function, and reduce reliance on rescue inhalers. In short, Budecort inhaler encompasses budesonide delivery, requires proper inhalation technique, and influences long‑term disease control – a classic semantic triple that frames its role in respiratory care.
Key points about Budecort inhaler
Using the Budecort inhaler correctly starts with a slow, deep breath followed by a one‑second hold; this simple step maximizes drug deposition in the lower airways. Typical adult dosing ranges from 200‑400 µg twice daily, but physicians may adjust the amount based on symptom severity, lung function tests, and exacerbation history. Compared with combination products like Symbicort, which adds a long‑acting bronchodilator, Budecort focuses solely on inflammation, making it a good choice for patients who need steroid coverage without extra beta‑agonist exposure. Common side effects include hoarse voice and oral thrush, so rinsing the mouth after each dose is recommended. The device’s portability and dose counter also support adherence, a factor that directly correlates with reduced hospital admissions – another semantic link: proper inhaler technique reduces exacerbation risk.
Choosing the right inhaler involves weighing disease stage, comorbidities, and personal preferences. For mild to moderate asthma, Budecort inhaler often serves as the baseline controller, while severe cases may require higher‑dose steroids or combination therapy. In COPD, it’s used to lower the frequency of exacerbations, especially in patients with a history of frequent hospital visits. Monitoring should include periodic spirometry, symptom diaries, and checking for steroid‑related systemic effects. Health‑care providers play a critical role in educating patients, reviewing technique at each visit, and adjusting the regimen as needed. With the right approach, Budecort inhaler can keep airways clear, improve quality of life, and lower health‑care costs. Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive deeper into dosage strategies, side‑effect management, and comparisons with other inhaled therapies.
Budecort Inhaler vs Other Budesonide Options: Detailed Comparison
A comprehensive side‑by‑side look at Budecort inhaler versus fluticasone, beclomethasone, Montelukast and other asthma options, covering efficacy, cost, safety and practical tips.