GLP-1 Agonist: What It Is, How It Works, and What You Need to Know
When you hear GLP-1 agonist, a type of medication that mimics the natural GLP-1 hormone to help control blood sugar and reduce appetite. Also known as incretin mimetics, it is used primarily for type 2 diabetes and, more recently, for chronic weight management. These drugs don’t just lower blood sugar—they change how your body handles food, hunger, and fat storage. That’s why they’ve become so popular, not just for diabetics but for people looking to lose weight too.
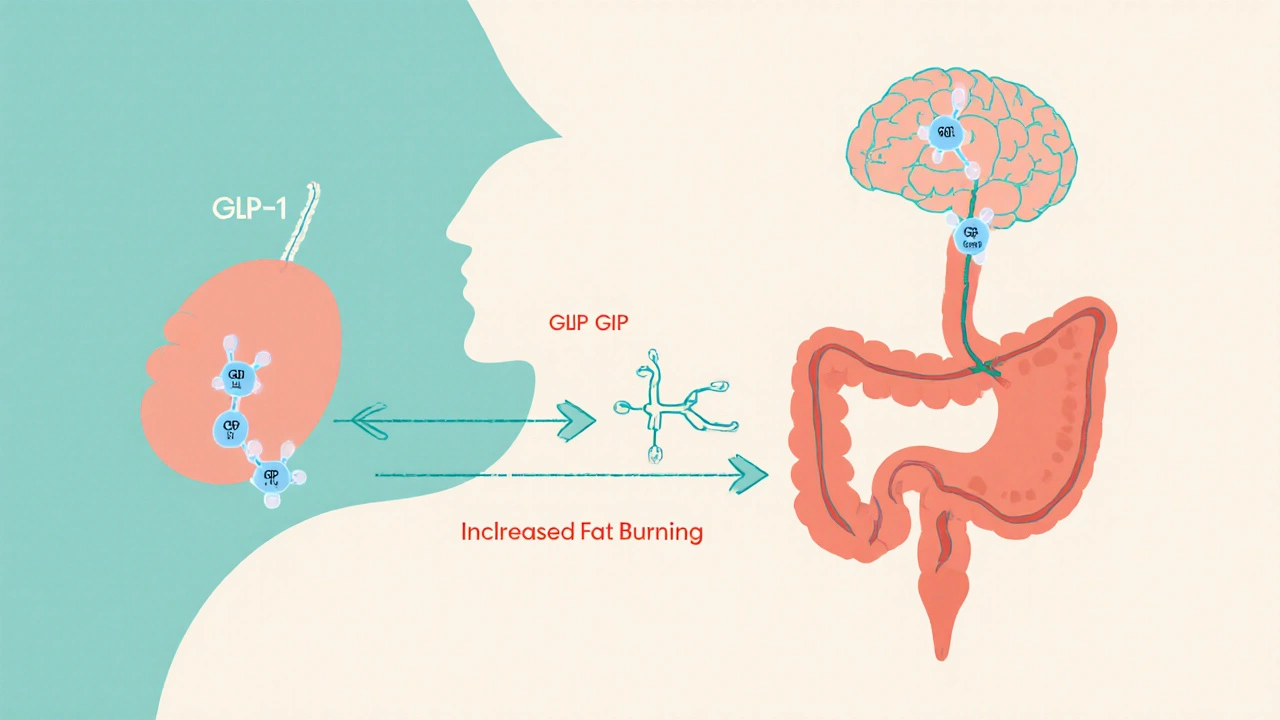
GLP-1 agonists work by activating receptors in your pancreas, brain, and gut. In the pancreas, they tell your body to release more insulin when blood sugar rises. In the brain, they help you feel full faster and stay full longer. In the gut, they slow down how fast food moves through your system. This combo means fewer blood sugar spikes, less hunger, and often, noticeable weight loss. You’ll find these effects in real-world use—not just in studies. People on drugs like semaglutide, a once-weekly GLP-1 agonist approved for both diabetes and weight loss and liraglutide, a daily injection originally developed for diabetes but now widely used for weight management report losing 10% or more of their body weight over time.
Not everyone responds the same way. Some people see dramatic results; others feel little change. Side effects like nausea, vomiting, or constipation are common at first, but they usually fade as your body adjusts. These drugs aren’t magic pills—they work best when paired with lifestyle changes. And while they’re safe for most, they’re not for everyone. People with a history of certain thyroid cancers or pancreatitis should avoid them. You’ll also need to know how to store them, how often to take them, and what to do if you miss a dose.
The posts below cover real questions people have: how GLP-1 agonists compare to other weight loss drugs, what side effects to expect, how they interact with other meds, and why some people stop taking them. You’ll also find comparisons with related treatments like SGLT2 inhibitors and what to do if you’re struggling with nausea or blood sugar swings. This isn’t theory—it’s what people are actually experiencing, asking about, and managing day to day.
Tirzepatide for Weight Loss: How Dual Incretin Therapy Works
Tirzepatide (Zepbound) is a dual incretin therapy that targets GLP-1 and GIP receptors to promote significant weight loss. With up to 22.4% body weight reduction in trials, it's more effective than single-receptor drugs like semaglutide.