AUD Treatment: What Works, What to Avoid, and How to Stay Safe
When someone struggles with alcohol use disorder, a medical condition where drinking causes harm to health, relationships, or daily life. Also known as alcohol dependence, it's not a moral failing—it's a treatable condition that often needs medical support. Many people try to quit on their own, but without proper care, withdrawal can be life-threatening. That’s why AUD treatment isn’t just about stopping alcohol—it’s about managing the physical and mental fallout safely.
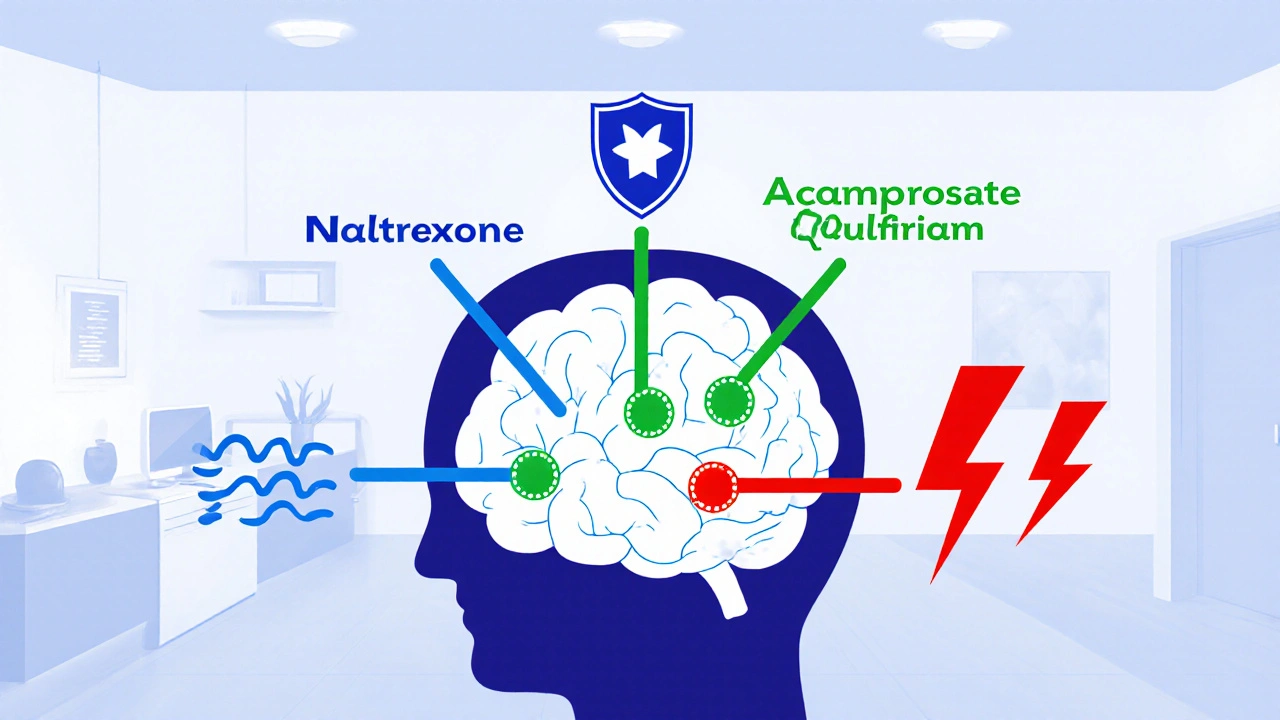
Effective AUD treatment often involves more than counseling. It includes monitoring for alcohol withdrawal, a sudden physical reaction when someone who drinks heavily stops or cuts back. Also known as detox syndrome, it can trigger seizures, confusion, or heart rhythm problems. That’s why medical supervision matters. Some people need medications like benzodiazepines to prevent complications, while others benefit from longer-term options like naltrexone or acamprosate. But here’s the catch: mixing these with other drugs—like acetaminophen or opioids—can wreck your liver or cause overdose. You can’t treat AUD in a vacuum. You need to know how it interacts with everything else you’re taking.
Your liver takes the biggest hit during AUD treatment. If you’ve been drinking for years, your liver might already be damaged. That means even common painkillers like acetaminophen can turn toxic. And if you’re using sedatives or antipsychotics for anxiety or depression, those can pile up and slow your breathing. medication safety, the practice of using drugs in a way that minimizes harm and avoids dangerous interactions. Also known as pharmacovigilance, it’s not just for doctors—it’s your responsibility too. That’s why posts here cover black box warnings, drug interaction tables, and why combining acid reducers or decongestants can backfire. You need to understand what’s in your medicine cabinet before you start AUD treatment.
Recovery isn’t linear. Some people relapse. Others get stuck managing side effects like constipation from naltrexone or drowsiness from gabapentin. That’s why knowing how to spot early warning signs of liver damage, kidney stress, or heart rhythm issues is just as important as knowing which pill to take. The articles below give you real, no-fluff details on what works, what’s risky, and how to protect yourself at every step. Whether you’re starting treatment, supporting someone who is, or just trying to avoid the next mistake—this is the practical guide you need.
Medications for Alcohol Use Disorder: How They Reduce Relapse Risk - and When They Don’t
Naltrexone, acamprosate, and disulfiram can reduce relapse risk in Alcohol Use Disorder - but only if used correctly. Learn how they work, who they help, and why so few people get them.