Drug Shortages: Why They Happen and How They Impact Your Medications
When a drug shortage, a situation where the supply of a medication doesn’t meet patient demand. Also known as medication shortages, it often means pharmacies can’t fill prescriptions on time—even for life-saving drugs. This isn’t rare. In 2023, over 300 drugs in the U.S. faced shortages, from antibiotics to insulin and even basic IV fluids. These aren’t just inconveniences. They force doctors to switch patients to less familiar drugs, delay treatments, or push people toward more expensive alternatives.
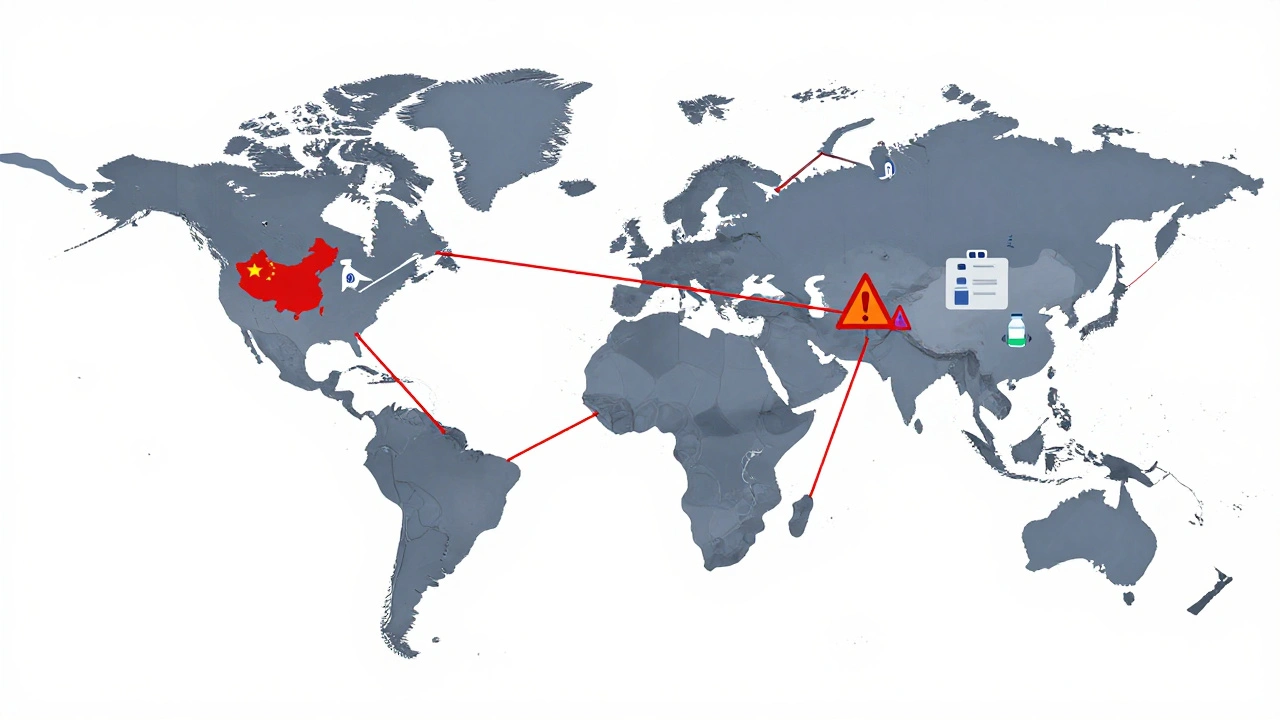
Behind every pharmaceutical supply chain, the network of manufacturers, distributors, and regulators that get drugs from labs to pharmacies. is a fragile system built on thin margins. Generic drugs, which make up 90% of prescriptions, are made for pennies. A single factory shutdown—due to quality issues, natural disasters, or raw material delays—can ripple across the country. One plant in India or China that stops producing active ingredients can leave thousands without their blood pressure or diabetes meds. And when manufacturers cut corners to save costs, the FDA steps in, halting production until problems are fixed. That’s when shortages turn into crises.
generic drug shortages, the most frequent type of drug shortage, affecting everyday medications like metformin, amoxicillin, and levothyroxine. are especially common because no one makes a profit on them. Companies don’t invest in backup production lines or extra inventory. When demand spikes—like during a flu season or a new guideline recommending a drug—there’s no buffer. You might find your pharmacy switching your levothyroxine brand without telling you, or your doctor prescribing a different antibiotic because the usual one is out of stock.
It’s not just about running out. It’s about safety. Switching meds can mean new side effects, bad interactions, or doses that don’t work as well. A patient on lithium might get a different version that changes blood levels. Someone on a blood thinner might get a substitute that doesn’t dissolve the same way. These aren’t theoretical risks—they’ve caused hospitalizations and deaths.
But you’re not powerless. Pharmacists track these shortages daily. They know which brands are available, when shipments are coming, and what alternatives work. The drug shortages you hear about in the news are often the tip of the iceberg. Behind the scenes, pharmacies are juggling options, calling distributors, and working with doctors to keep patients covered. That’s why calling your pharmacy before your refill runs out matters. It’s not just about getting your pills—it’s about staying safe when the system is under pressure.
Below, you’ll find real guides on how to spot when a medication change could hurt you, how to use FDA tools to track safety alerts, and how supply chain decisions affect what’s on your shelf. These aren’t abstract theories. They’re the tools patients and pharmacists use every day to navigate a broken system—and keep getting the meds they need.
International Supply Chains: Why Foreign Manufacturing Is Causing Drug Shortages in 2025
International supply chains for pharmaceuticals are under strain, causing widespread drug shortages in 2025. Over 80% of active ingredients come from China and India, making the system vulnerable to disruptions. Here’s how it’s happening-and what’s being done to fix it.